IT services are paramount in helping businesses streamline their operations and scale. Since IT encompasses a broad range of practices and disciplines, keeping up with the terminologies can be intimidating. Here’s our glossary to help guide you through the essential terminologies and premises of the IT industry.
Information technology is a vast field that touches on many technicalities including communication, data, and systems. It’s extremely diverse and filled with a ton of lingo and concepts that can be intimidating to grasp at first.
In this glossary, we’ll run through the important lexicon so you’ll know what they mean when you encounter them in practice.
Looking for a IT Services agency?
Compare our list of top IT Services companies near you
Trying to look for an experienced service provider for your business? Connect with the leading IT service companies on Clutch.
80 IT Services Terms You Need To Know
From A to Z, each vocabulary here is commonly used within the IT service sphere. Explore these terms and definitions we’ve curated for you.
A
- Access Point: A hardware that serves as the base point where wireless devices connect and transfer data to a wired network.
- Algorithm: In computer science, algorithms are a series of orders set to solve specific computational problems or perform certain functions.
- API: Stands for Application Programming Interface — it is a set of rupees that enable various applications to connect and communicate with each other. It allows businesses to perform day-to-day tasks and transfer data.
- APT: Stands for Advanced Persistent Threat — intricate hacking techniques that are consistent and illicit. It carefully targets sensitive and potentially destructive data from large enterprises or government systems.
- Artificial Intelligence: Also known as AI, artificial intelligence is a simulation of human intelligence in machines programmed to rationalize and act like human beings.
- Authentication: The process of confirming or verifying the credentials of the user or device before granting access to certain resources or systems.
- Automation: The process of developing a system to handle repetitive processes or tasks, replacing the need for manual work and minimizing human input.
How much do IT projects cost? Learn the cost of an IT services engagement.
B
- Bandwidth: It is the measure of how much data transfer capacity a network has. Typically, the higher the bandwidth, the faster devices can transmit information from the internet.
- Biometric Authentication: This refers to a security procedure that requires the biological characteristics of individuals to verify their identity. Often, biometric authentication uses fingerprints, iris scans, or facial features to check data.
- Business Applications: It refers to a collection of important applications or systems that help run businesses. They can be used by business owners, employees, suppliers, and even customers.
- BYOD: Stands for Bring Your Own Device — it is a setting where employees are asked or required to use their personal devices for work functions.
C
- Cache: A hidden space embedded within computer memories that temporarily stores data that can be accessed faster than main memory.
- Cloud Computing: It is a general for everything that requires delivering hosted solutions over the internet; this includes tools, databases, software, and storage.
- Compliance Management: This refers to the process of monitoring and tracking an organization’s procedures, systems, and policies in order to make sure employees adhere to regulations, accreditations, and codes.
- Computer Network: A group of connected computing devices that transmit data and resources to each other via cable or wireless media.
- Computer System: This is the basic, complete setup of hardware and software needed to perform computing operations.
- Cyberattacks: An assault by hackers to gain unauthorized access to a computing network or system and extract information with the intent to cause damage.
- Cybersecurity: The practice of protecting computer networks, programs, and data from malicious attacks from hackers.
Additional reading: “How to Create a Cybersecurity Budget [with Template]”
D
- Database: An organized collection of structured data records or information for easy access, tracking, and updating.
- Data Center: A physical location or facility that is designed to serve as the central depot of storage systems, complex networks, and computing infrastructure. It’s an important asset that allows organizations to process, access, and transmit large volumes of data.
- DLP: Stands for Data Loss Prevention — it is a set of processes and tools that secures sensitive data, preventing it from being misused or accessed by unauthorized users.
- Data Storage: A general term widely used for recording, retaining, and preserving data using computing devices.
- Disaster Recovery: The ability of an organization or team to recover access to its IT infrastructure in an event of a cyberattack, natural disaster, or unforeseen disruptions.
- DNS: Stands for Domain Name System — this translates human words and matches them to corresponding IP addresses. Essentially, it maps the names typed by people on search bars to find the website.
E
- Edge Computing: A distributed computing framework that enables remote devices to process data as close to the originating point as possible. Rather than communicating raw data, it processes information in real-time locally, reducing bandwidth.
- Endpoint: The physical device that communicates information back and forth with a computer network. Mobile phones, desktop computers, and servers are some examples of endpoints.
- End-user: The person to whom the product was intended to be used or consumed.
- Ethernet: A networking technology designed to connect devices in a wide area network or local area network. The ethernet can use both wired and fiber cables to deliver data and power.
F
- Firewall: This refers to the network security device that tracks all incoming and outgoing traffic, and filters them based on specific security policies set. Essentially, it acts as a barrier between private internal networks and the public internet.
- FTP: Stands for File Transfer Protocol — a network protocol that transfers, downloads, and uploads data between computer systems. Originally, it was designed to transfer information between two physical devices, but now, it’s also widely used to store data in the cloud.
G
- Gateway: A computer that’s between different networks or applications which converts data from one protocol to another. It’s a network code that serves as the entry and exit point, looking through all the data that passes through.
- GPS: Stands for Global Positioning System — is a US-owned radio navigation system that’s made up of a network of satellites and receiving devices. It is commonly used to determine the exact location of a device on earth.
H
- Help Desk: An individual or team that’s function is to provide assistance or information to computer users within an organization.
- HCI: Stands for Hyper-converged Infrastructure — is a software-centric IT architecture that integrates all aspects of a traditional data center. Essentially, it’s deployed as a ready-to-work data center but in a more compact form.
- HTML: Stands for Hypertext Markup Language — this is a popular markup language for documents designed to be viewed in a web browser. It is the most basic building block of the web.
I
- IAAS: Stands for Infrastructure as a Service — a type of cloud computing service that allows enterprises to lease their virtualized servers and networking resources on-demand online. It allows users to run applications and operating systems, giving them more flexibility without the responsibility of manually setting physical servers.
- IoT: Stands for Internet of Things — it is an interconnected network of physical objects embedded with chips, sensors, and other technologies that allow them to transmit data over the internet.
- IP Address: Stands for Internet Protocol Address — it is the unique numerical address assigned to every device and network, allowing them to connect to the internet and send and receive data.
- ISO: Stands for International Organization for Standardization — it is a Geneva-based organization that works in 167 countries to facilitate world trade and provide common standards for all fields including technology.
- IT Infrastructure: This refers to every component that makes up an IT or IT-powered operation. It is all of the fundamental hardware and software that enables the flow, storage, and processing of information.
J
- Java: A popular high-level, class-based, object-oriented programming language that’s widely used as the server-side language for many backend development projects.
- JavaScript: A famous programming language that is one of the foundations of the World Wide Web. It’s used by developers to create dynamic solutions, multimedia, and interactive web pages.
K
- Knowledge Base: Refers to the end results or product of collecting and organizing important data, acting as a self-serve online directory. A knowledge base may consist of FAQs, runbooks, troubleshooting guides, and other data that people within an organization may need or want to know.
L
- LAN: Stands for Local Area Network — a collection of connected devices that form an organized network within a limited location. Typically, a LAN will be exclusive to a particular school, office, or church.
- Lifecycle: Otherwise referred to as product lifecycle, it is the course of action and stages of a product or service. Lifecycles follow the beginning of the product when it’s being conceptualized, to its development, and to its eventual decline.
Source: Investopedia / Xiaojie Liu
- LOB Application: Stands for Line of Business Application — the term that describes all of the computer applications that are essential to the operations of an organization. They are typically larger, complex programs that are capable of many functions and are linked to the organization’s databases.
M
- Machine Learning: A subset of artificial intelligence that enables software applications to accurately predict outcomes using data and algorithms.
- Malware: It is an umbrella term for all forms of malicious software that aims to exploit or cause damage to any device, network, or program. Cybercriminals utilize it to gain sensitive information that they can use against organizations in exchange for ransom.
- Man-in-the-Middle Attacks: It is a type of hijacking or eavesdropping attack where cybercriminals move to intercept data transfer between two parties while sending malicious links to them.
- Microsoft: A multinational technology company that produces software products used in cloud computing, gaming hardware, and communication.
- MSP: Stands for Managed Service Provider — a service provider that remotely supports and manages an organization’s information technology infrastructure and systems. They offer technical solutions, fix services, and other non-customer-facing functions.
Additional reading: “When to Hire an Inhouse IT vs. Managed Service Provider (MSP)”
N
- Network Adapter: A component within a computer’s hardware that allows it to communicate to another computer or server through a local area network.
- NOC: Stands for Network Operations Center — it is the main location where computer, satellite, and telecommunications systems are monitored and maintained.
- NIST Compliance: This means adhering to the security standards and industry practices set by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). The standards are endorsed by the US government and it is designed as a framework to protect crucial information.
O
- Open Source: Otherwise known as Open Source Software (OSS), it is software with source code that any developer can use, modify, or copy.
- OS: Stands for Operating System — it is the system software that manages all of the applications in a device. It controls the memory and processes of the device’s hardware and software resources.
P
- PAAS: Stands for Platform as a Service — a platform-based solution that provides an environment for developers and organizations to build, run, and deploy applications more efficiently and cost-effectively.
- Personally Identifiable Information: Refers to the information that verifies the identity of a user. Also called PII, it may contain direct identifiers such as ID information or quasi-identifiers such as race.
- PSA Software: Stands for Professional Services Automation Software — a solution that offers a range of different tools for project management, tracking, planning, and collaboration. It’s designed to help service providers throughout the lifecycle of a project.
Q
- QA: Stands for Quality Assurance — it is a meticulous systematic process that gauges whether the product or service meets the standards and requirements.
- QoS: Stands for Quality of Service — a set of technologies that measure the overall performance of a service and determine its reliability to run crucial programs and data flows within limited network performance requirements.
R
- Risk Management: It refers to the deployment of specialized methodologies, policies, and practices to manage and avoid IT threats.
- Routers: A hardware that connects a modem to other devices, allowing them to communicate between the devices and the internet.
- RPO: Stands for Recovery Point Objective — it determines the maximum data loss tolerance after a network or system unexpectedly goes down or fails. It functions by indicating the time frame before the volume of data loss exceeds the limits authorized by a business continuity plan.
S
- SaaS: Stands for Software as a Solution — a software-based distribution model that hosts and offers applications to organizations over the internet through subscription basis or licensing agreements.
- SLA: Stands for Service-Level Agreement — it’s the proven level of service expected by customers from a service provider or supplier. It outlines the metrics that need to be met by the service provider and the following fines or actions should the agreed-upon service is not achieved.
- SOC: Stands for Security Operations Center — is an in-house or outsourced team that’s dedicated to monitoring an organization’s IT infrastructure security from top to bottom. They are responsible for 24/7 support, detecting possible vulnerabilities, and responding to cybersecurity incidents.
- Software Development: The process where developers design, create, and launch computer programs using specific programming languages such as Java, Python, C++, and Scala.
T
- Telecommunications: Also known as telecom, it is a broad term that describes the electronic exchange of data over vast distances.
- Two-factor authentication: Otherwise called 2FA, it is a dual-factor management security process that requires users to complete two identification methods to authenticate their credentials and access resources.
U
- UTM: Stands for Unified Threat Management — it refers to a single hardware or software solution that performs multiple security functions, combining management and compliance capabilities to make it easier for administrators and IT teams. It provides protection against spyware, viruses, network attacks, and other malware.
V
- VDI: Stands for Virtual Desk Infrastructure — it is a technology that allows employees to access work programs and applications remotely from outside of the office.
- VoIP: Stands for Voice over Internet Protocol — it is an internet telecommunications system that allows users to make and receive voice calls online rather than via conventional landline networks.
- VPN: Stands for Virtual Private Network — a service that enables secure and private network connection to the internet using an encrypted tunnel to hide IP addresses and other personal data.
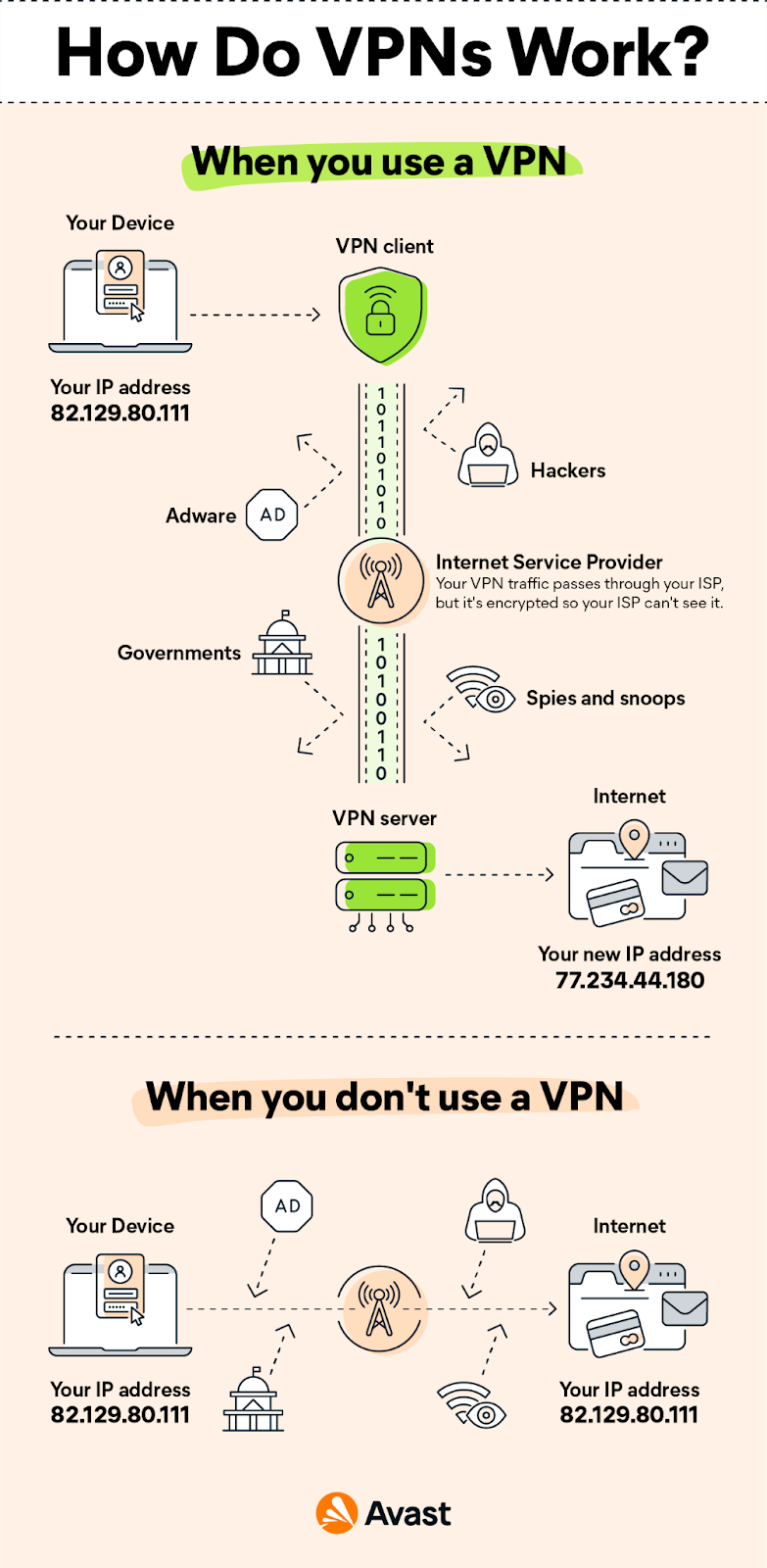
Source: Avast
- Vulnerabilities: This refers to any weaknesses in a computer system or network of an organization. Vulnerabilities are generally targeted by cybercriminals lurking and looking to exploit sensitive data.
W
- WAN: Stands for Wide Area Network — it is a vast network of data that is not restricted to a single geographical location. They can facilitate the communication of information between multiple devices around the world
- Web Browser: An application program that allows end users to access and interchange information across the World Wide Web.
- Wi-Fi: Stands for Wireless Fidelity — it is a technology that’s widely used to connect devices such as computers, mobile phones, and tablets to the internet. It is the radio signal that’s transmitted by a wireless router to connected devices.
X
- XDR: Stands for Extended Detection and Response — it is a multilayered tool designed to detect, investigate, and respond to threats efficiently.
Z
- ZTNA: Stands for Zero Trust Network Access — it is a sophisticated security solution that remotely accesses an organization’s applications, programs, and data, operating on an adaptive trust model.
Knowing the Context Makes A Difference
Context is key. Understanding the basic meaning of these terminologies can help you avoid confusion when setting up an IT infrastructure or when working with a service provider. Given that there are many different technical words and the fact that the industry constantly progresses, it’s understandable that it may take a while to learn most of them.
In search of a partner that you can rely on for IT support? Get in touch with the best IT service providers and companies on Clutch.
About the Author
Elaine Margrethe Alcantara
Elaine Margrethe is a part of Clutch’s global team of writers. She is responsible for writing blogs, supporting blog processes, and content creation efforts.
See full profile






