Updated February 16, 2026
While AI is helping companies across every industry improve their productivity, make smarter business decisions, and unlock new opportunities for innovation that were previously locked away in their data, bad actors are also leveraging AI to create more advanced cyber threats.
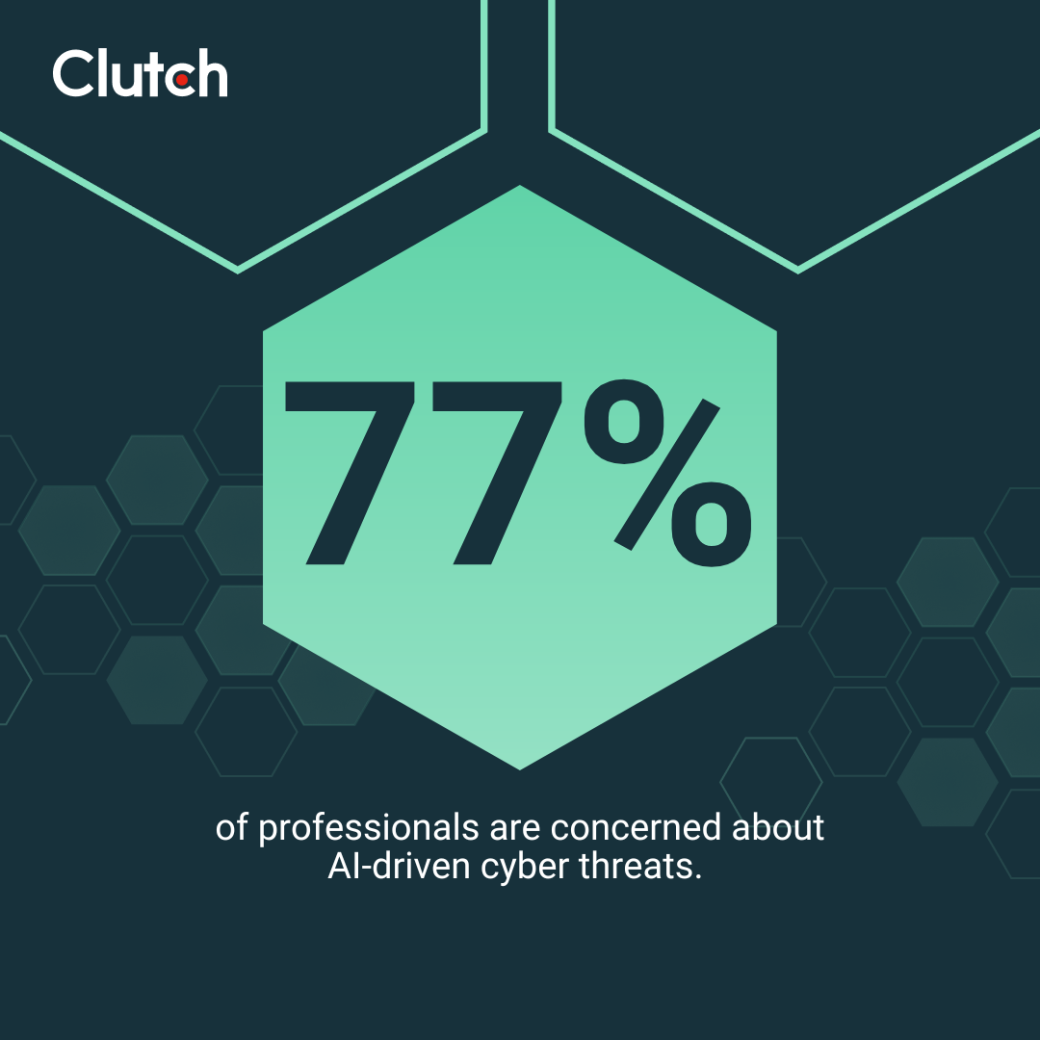
From generative AI tools that enable subtler phishing attempts to machine learning (ML) tools that let malware adapt to cyber defenses, AI has made modern cyber attacks faster, more convincing, and harder to detect than ever — and traditional cybersecurity methods are struggling to keep up. That's why 77% of professionals are concerned about AI-driven cyber threats.
Looking for a IT Services agency?
Compare our list of top IT Services companies near you
This article will examine the relationship between AI and cybersecurity. First, we'll explain why AI-driven cyber attacks are more dangerous than conventional threats and how businesses face greater challenges to their operations because of them. We'll also explore how businesses are responding to the threat of AI cyber attacks and how working with the right B2B provider can help.
AI can help employees work faster and smarter than they could with manual processes — and the same is true for threat actors. AI-powered cybersecurity attacks can launch faster, disguise themselves more convincingly, and escape detection better than manual threats. This makes them harder to identify, contain, and remediate, and forces cybersecurity experts to strengthen their defenses if they hope to keep up.
AI cyber attacks execute and scale faster than their manual counterparts. Like all AI tools, AI-powered malware can scan massive datasets more quickly than humans ever could, and it can analyze patterns in network traffic to learn how to penetrate cyber defenses. These tools can identify vulnerabilities across thousands of systems, letting them pick the easiest route to exploit.
For example, some AI tools enable faster brute-force attacks by quickly deciphering passwords, making detection more difficult. AI-based reconnaissance tools scan for system vulnerabilities instead of launching an immediate attack, giving the cyber threat a clearer picture of how they should strike.
Just as generative AI tools can be used to create personalized messages or compelling images for marketing or sales campaigns, they can also be used to craft carefully tailored phishing emails or social engineering attacks. They do so by analyzing social media, emails, and internal communications to identify speech or writing patterns so they can mimic them to make their attacks sound more convincing.
For example, AI-powered spear-phishing attacks may detect certain references to specific projects or executives, and may mention them in their messages, causing employees to believe the email comes from a legitimate source. Deepfake technology can also compile false audio and video files, creating scenarios that never occurred. This can persuade an employee to perform an action, such as transferring funds or clicking a link, under the belief that they were following directions.
Such personalized AI cyber attacks can be highly deceptive, so education on how to detect them is crucial.
AI cyber attacks are more agile and therefore harder to stop. For example, polymorphic malware alters its code each time upon execution, helping it avoid the signature-based detection mechanisms that anti-virus programs use to respond to a threat. They can also learn from security tools’ responses and modify their behavior to avoid detection in future attacks.
The advanced capabilities of AI cyber attacks have created new challenges for businesses, especially as they bring employees who are less familiar with AI up to speed with the technology. A few cybersecurity-related obstacles that companies must tackle are:
Taken together, companies face more sophisticated threats from more directions than they have in the past, making their attack surface far more difficult to manage. AI can be just as powerful for stopping a cyber attack as it can for launching one, but the first line of defense will always be your people.
Nearly half (49%) of small businesses report phishing and impersonation is their top concern with AI-driven cyber threats.

While AI cyberattacks, such as brute-force tools and polymorphic malware, are a significant threat to today's cybersecurity systems, advanced phishing and impersonation attempts are still the biggest threat — and by a wide margin. Phishing attempts were the start of 80%–95% of all cyberattacks as of 2023, and in 2024, 10% of companies experienced a deepfake attack. Such realistic AI-generated emails, messages, and video calls are highly effective at tricking employees, and their legitimacy lets them bypass traditional spam filters, making them even more persuasive.
Despite such a dangerous threat landscape, the leading companies are still finding ways to maintain their cyber defenses. A multi-layered security strategy can help ward off diverse types of incoming threats. And while AI can be used for good in the battle for cybersecurity, employee training is still the best way to prevent a breach.
A well-educated workforce is less likely to succumb to social engineering attempts, so train your team on how to spot an attack. A few tactics for resisting phishing attempts are:
By teaching your employees to regulate their emotions, look for signs of fraud, and think critically about the attack requests, they'll be better equipped to ward off a threat, and your network can remain secure.
With many anti-virus and firewall tools no longer able to keep pace with such intelligent cyberattacks, AI has become a leading cyber defense. AI-powered cybersecurity tools come in many different forms and have a wide range of functionalities, such as:
AI-powered cybersecurity tools are particularly effective at detecting a deepfake. By employing advanced analytics and machine learning algorithms, they can identify unusual communication or visual patterns at the pixel or decibel level. This makes them much more accurate than the most astute human observers — proof that it takes AI to counter AI.
There is no one-size-fits-all approach to cybersecurity. Different cybersecurity tools are needed to thwart different cybersecurity attacks, so teams must build multiple layers into their defenses. They can do this by combining the leading technologies with best practices and encouraging cyber vigilance from every team member involved.
Conducting regular incident response planning sessions also helps ensure that the proper protocols are followed if an incident occurs, and regularly updating your security policies can keep your defenses current with the newest cyber threats. A holistic approach to cybersecurity is always best for guarding against advanced AI-powered threats, and a strategy that integrates cutting-edge technology, safe cybersecurity processes, and workforce education is the right way to create such a defense.
The relationship between AI and cybersecurity is complex, with AI being both the cause and the cure to the leading cybersecurity challenges. Polymorphic malware and brute-force attack tools are just a few AI-powered cyber threats, and deepfake technology has made phishing attempts more compelling than ever. These advancements have created new challenges for security teams to solve, but employee education, AI-powered security tools, and a multi-tiered approach to cybersecurity can still keep your network safe.
Working with a cybersecurity expert can also be a great way to identify your vulnerabilities and strengthen your cyber defenses. As the leading marketplace for B2B service providers, Clutch is the place for companies to find the best firms for cybersecurity projects. Reach out today to find a provider that can elevate your AI cybersecurity and maintain your defenses in an evolving digital world.