App development is a technical field, so it can be difficult to feel comfortable in conversations about it without a common vocabulary. This glossary will help you understand the most important terms and concepts in the industry.
Whether you’re researching a software application, mobile application, or web application, it’s easy to get caught up in a sea of technical terms and acronyms if you’re not intimately familiar with the field.
This glossary will overview and define various essential development tools, mobile operating systems, and processes performed by development teams to create specific platforms for end users.
Looking for a Mobile App Development agency?
Compare our list of top Mobile App Development companies near you
Looking for help creating an app of your own? Find top app development companies on Clutch.
64 App Development Terms to Know
It doesn’t matter where you are in your understanding of the app development lifecycle, there are almost always new things to learn about this evolving industry.
A
- Agile: A development methodology known for prioritizing iteration and flexibility, breaking down work milestones into collaborative development ‘sprints’.
- API: Stands for Application Programming Interface — operates as a middleman between two applications, allowing them to work together and functionally integrate.
- APK: Stands for Android Package Kit — the type of file used for applications' code on Android operating systems. APK files function within the Android Studio IDE.
- App Store: A marketplace for applications that can be accessed on smartphones and web browsers — typically refers to either the Apple App Store or the Google Play store.
B
- Beta Testing: A pre-release version of an app that is made available to a select group of users to test. This phase of testing helps software development companies find bugs or inefficiencies before the final version of the app goes to market.
- Backend: The server side of an application that handles data storage, processing, and retrieval.
- Bug: An error or flaw in an app that causes malfunctions or undesired results.
C
- Cache: A temporary storage location for frequently accessed data that speeds up an app's performance.
- CDN: Stands for Content Delivery Network — a network of servers designed to reduce the time needed to access content by caching content in servers close to where the information is being accessed. Content starts within an ‘origin server’ and is later copied to other servers to expedite retrieval times.
- Code Review: The process of reviewing and critiquing an app's code for errors and potential improvements — part of the QA process.
- Content Management System (CMS): a type of application that allows multiple users to create, edit, publish, and manage written and visual content on a website.
- Cross-Platform App: An app that can run on multiple platforms, such as Android and iOS. This makes applications accessible to Mac and Microsoft-loyal buyers alike.
D
- Database: A structured collection of data that users can analyze, manipulate, and access through an application or platform.
- Debugging: The process of identifying and fixing bugs in an app's code, often carried out by development teams or QA specialists.
- Deployment: The process of releasing an app or new features to users. Deployment plans account for executing changes in live environments as well, for apps that have already been released.
F
- Feature Creep: The tendency for an app's development to include too many unnecessary features, resulting in bloat and poor performance.
- Frontend: The client-side of an application that users interact with on mobile phones or web browsers.
- Framework: A pre-written set of code and libraries that simplifies app development — examples include React Native and Ionic.
Additional Reading: ‘How to Create a Budget for App Development'
G
- Git: A DevOps source code management tool that helps mobile app development teams track changes in code and manage code across multiple developers at scale.
H
- Hybrid App: An app that combines elements of both native and web apps, usually developed using HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
I
- IDE: Stands for Integrated Development Environment — a program that supports developers in creating code for application projects.
- In-App Purchase: A feature that allows users to buy content or services within an app that enhances the overall user experience or product enjoyment.
- iOS: The operating system used on Apple mobile devices, such as iPad and iPhone.
J
- Java: An Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) language commonly used for Android app development
- JSON: Stands for JavaScript Object Notation — a lightweight data-interchange format that can be analyzed by both development teams and machines. JSON is independent of all programming languages, able to function outside of Java.
K
- KPI: Stands for Key Performance Indicator — a measurable value that indicates how well an app is performing. Development teams select KPIs based on performance metrics and a company’s overall mission.
L
- Library: A collection of pre-written code that can be used in an application. This code is designed to be reusable and applicable for a myriad of use cases.
- Localization: The process editing certain features of an app to make it naturally blend in with different languages and cultures. Localization requires translation software and analytics to be done effectively.
M
- Middleware: A layer of code between an app’s front end (client side) and its back end (server side). Middleware provides a secure platform for communication between the two sides.
- Mobile App Development: The process of creating a mobile app, which requires knowledge of user interface and experience design, coding languages, databases, performance metrics, security measures and more.
- Mockups: A static representation of a proposed design, used to test user interface and experience before the actual development takes place. Mockups help developers anticipate concerns from users.
- MVP: Stands for Minimum Viable Product — a version of an app with only its essential features. MVPs are used to quickly test an idea with users before investing more time and money in development.
- Multi-Device Optimization: Optimizing a website or app for use across different devices, including smartphones, desktop computers, and more.
N
- Native App: An app developed specifically for a single platform, like Android or iOS. Native apps are usually faster and more reliable than web apps because they're built specifically for a single platform.
Additional Reading: ‘How to Decide Between Native and Hybrid Mobile Apps’
O
- Objective-C: A general-purpose programming language that utilizes Smalltalk-style messaging for programming using C, which is the main language used to create applications for iOS.
- Open Source: A software development approach where the source code is available for anyone to view and modify. Open source software is usually free to use and has a large community of developers contributing to its development.
- OTA: Stands for Over-the-Air — the process of updating an app wirelessly. OTA updates are used by developers to make changes and additions to their apps without requiring users to download a new version from the App Store.
P
- PaaS: Stands for Platform as a Service — a platform that allows developers to build, manage, and deploy applications without having to worry about the underlying infrastructure required with more traditional platform options.
- Parse: A backend service that simplifies data storage and user authentication for mobile apps. It is available in a hosted form (Parse Server) as well as an open-source version.
- Prototypes: A first version of an application needed to test and evaluate features before launching the final product. Prototyping tools such as InVision, Sketch, and Figma make constructing prototypes more faster for dev teams.
- Push Notification: A message sent to a user's device to inform them of new content or updates in an app. Push notifications can be sent via SMS, email, or a push notification service provider.
Q
- Quality Assurance (QA): The process of ensuring that an application meets its requirements and works as expected. QA involves testing, debugging, and other activities to ensure the quality of the software. QA also involves code review and automated testing.
R
- React Native: A JavaScript framework used for developing mobile applications. It is based on React, a popular library used by developers to build user interfaces (UIs). React
- REST: Stands for Representational State Transfer — a software architectural style for building web services. RESTful web services use HTTP requests to perform actions (such as create, read, update, and delete) on the server.
S
- SEO: Stands for Search Engine Optimization — the process of optimizing a website or web page to rank higher on SERPs (Search Engine Results Pages). SEO involves various activities, such as keyword research, content optimization, and link building.
- Server-Side Rendering: The process of generating HTML code on the server before sending it to the client’s browser. Server-side rendering can improve page load times and make websites more responsive
- SDK: Stands for Software Development Kit — a set of tools that developers can use to create applications, such as software libraries, code samples, and documentation. SDKs are usually specific to one programming language or platform.
- Simulator: An emulator that mimics the behavior of an app on a specific device. Simulators are often used by developers to test their apps on different devices without having access to the physical device itself.
- SQL: Stands for Structured Query Language — a language used for managing and querying databases
- SSL: Stands for Secure Sockets Layer — a protocol used to encrypt data transmitted over the internet. SSL helps to protect data from being intercepted by malicious users or hackers.
- Stack: A collection of software tools used in app development. Examples of stacks include the LAMP stack (Linux, Apache, MySQL, and PHP) or the MEAN stack (MongoDB, Express, AngularJS, and Node.js).
- Swift: An open-source programming language created by Apple for developing iOS, macOS, watchOS and tvOS apps.
T
- Testing: The process of evaluating an app's performance, functionality, and usability. Testing is either done manually by a QA team or through automated processes.
U
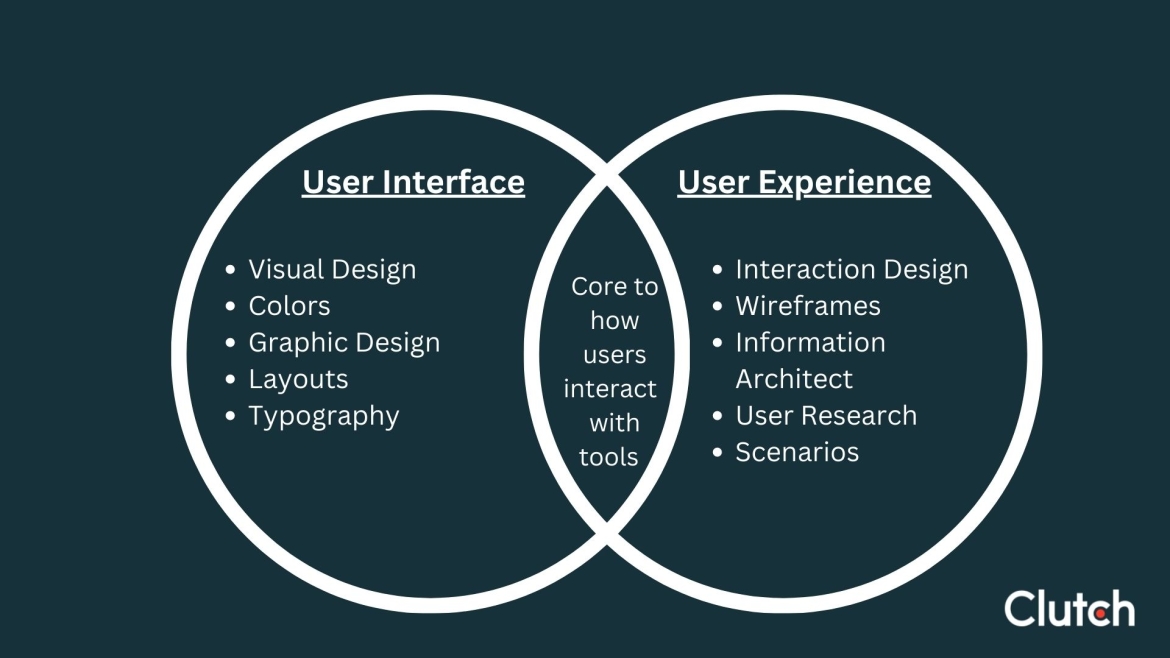
- UI: Steands for User Interface — the ‘look and feel’ of an app and the means and inputs that users leverage to engage with it.
- UX: Stands for User Experience — refers to how a user interacts with, and perceives an app or website. UX is concerned with making sure that the user's experience is efficient, effective, and enjoyable.
V
- Version Control: The management of changes to source code over time, usually using a version control system like Git. Version control allows teams to easily track changes, revert back to old versions, and collaborate on code with other developers.
- Virtual Machine: An emulation of a computer system that can run apps in a simulated environment, allowing developers to debug and work with their software without affecting the real world.
W
- Web Pages: Documents written in HTML, CSS and JavaScript that are published on the Internet. Web pages often contain interactive elements like buttons, forms, and navigation menus.
- WebView: A component that enables the display of web content within an app. WebViews are useful for displaying content from a website within an app, such as displaying a web page inside of a mobile app.
- Wireframes: A visual guide used to document the structure and layout of an app or website. Wireframes are often used in the early stages of development to determine how elements will be arranged on a page.
X
- Xcode: The IDE used for iOS app development. Xcode is used to write and compile code, manage source control and publish apps to the App Store.
Y
- YAML: A human-readable data serialization language. YAML is commonly used for configuration files and data storage in web applications.
Z
- Z-index: An attribute which determines the stacking order of HTML elements on a webpage. Z-index can be used to ensure that certain elements are always visible, regardless of their position or size on the pag
- Zero-Trust Network Security: A security model which focuses on authentication and access control, stating that external users should be denied access to internal networks by default. Zero-trust network security requires continual verification of identities and devices accessing the network.
Understanding the Components of the App Development Process is Excellent Context
The development industry can be particularly confusing to newcomers, especially given all of the new terms and phrases one must learn to get into the conversation. The truth is: anyone can keep up with the app development industry, so long as they’re willing to learn and build a development vocabulary.
Looking for a team to help you kick off a development project. Find the best app development companies on Clutch.
About the Author
Sydney Wess
SEO Manager at Clutch
Sydney Wess is a SEO manager who focuses on strengthening organic performance and building topical authority for Clutch.
See full profile





