
Updated May 7, 2025
In the digital world, when users expect instant replies and flawless interactions, optimizing your application's performance is important. A laggy or unreliable application may result in unhappy clients, abandoned shopping carts, and revenue loss. According to research, a mere 1-second lag in page load time can cause a 7% decline in conversion rates. This is where your product's responsiveness, stability, and scalability are vitally protected by QA performance testing.
This detailed article will discuss the fundamentals of QA performance testing and examine the critical indications you should watch to ensure your application's success in today's demanding digital market.
QA performance testing, often facilitated by specialized performance testing services, is a vital facet of QA testing that goes beyond mere functionality. It scrutinizes how an application behaves under varying load conditions, from expected user volumes to peak traffic spikes. This proactive approach, sometimes augmented with test automation services, measures responsiveness, stability, and resource utilization.
Essentially, QA performance testing unveils and rectifies performance bottlenecks, ensuring a smooth and satisfying user experience even when demand soars.
QA performance testing isn't a one-time event; it's a strategic process woven into the fabric of the software development lifecycle, ensuring optimal application performance under various conditions. Let's highlight the critical moments when this particular type of QA testing—which is occasionally supported by test automation services—takes center stage:
You can ensure that your application runs effectively and operates appropriately at these crucial points, giving your audience a smooth and positive user experience. This may be achieved by carefully including performance testing in your design.
| S.No. | Feature | Load Testing | Stress Testing |
| 1 | Purpose | Evaluates application behavior under normal and anticipated peak loads. | Pushes the application beyond its limits to identify breaking points and assess stability. |
| 2 | Load Conditions | Simulates expected user loads and traffic patterns. | Subjects the application to extreme load conditions, exceeding normal expectations. |
| 3 | Focus | Measures response times, throughput, and resource utilization under expected load. | Identifies the application's breaking point, failure behavior, and recovery capabilities. |
| 4 | Key Metrics | Average response time, peak response time, transactions per second (TPS), error rate, resource utilization. | Maximum concurrent users, time to failure, recovery time, error handling under extreme stress. |
| 5 | Benefits | Ensures the application meets performance expectations under normal conditions. | Provides insights into the application's robustness and resilience under extreme scenarios. |
| 6 | Automation Potential | High, often facilitated by test automation services. | Moderate, with some aspects requiring manual intervention and monitoring. |
| 7 | Relevance to QA Performance Testing | Essential for validating performance under expected conditions and identifying bottlenecks. | Crucial for ensuring the application can handle unexpected spikes in traffic and gracefully recover from failures. |
| 8 | Typical Scenarios | Pre-release testing, capacity planning, regular performance monitoring. | Disaster recovery testing, infrastructure stress testing, high-stakes application scenarios. |
Beyond mere functionality, QA performance testing, often bolstered by specialized performance testing services, delves into how an application responds under pressure. This assessment is guided by several critical metrics, which guarantee a smooth user experience even during peak loads.
This measures how swiftly the application reacts to user requests. Faster response times, often facilitated by test automation services, translate to a smoother, more satisfying interaction.
This determines how much work an application can do in a predetermined amount of time. Higher throughput, a key metric in QA testing, signifies greater capacity and efficiency.
This monitors the proportion of requests or transactions that fail. A low mistake rate indicates a solid and dependable program, which is important for user confidence.
This monitors how system resources like CPU, memory, and disk I/O are utilized. Efficient resource management, frequently supported by performance testing tools, is critical for achieving peak performance.
This identifies the number of concurrent users or requests that the program processes. Understanding how the application scales under different loads is critical to ensure constant performance.
By regularly monitoring these metrics, QA testing teams may proactively detect and fix performance bottlenecks, guaranteeing that the application runs properly and performs optimally under all conditions.
Metrics are the foundation of QA performance testing, providing measurable insights into how a web application behaves under stress. These metrics, which are frequently automated via test automation services, can identify bottlenecks and opportunities for improvement. Let's look at several significant metrics and their normal ideal ranges.
By meticulously maintaining these indicators, QA teams, often assisted by performance testing services, may proactively optimize application performance, ensuring a flawless experience for users even during high usage.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) in performance testing, often extracted using test automation services, act as beacons, guiding QA teams towards optimized application performance. However, their value hinges on context and interpretation.
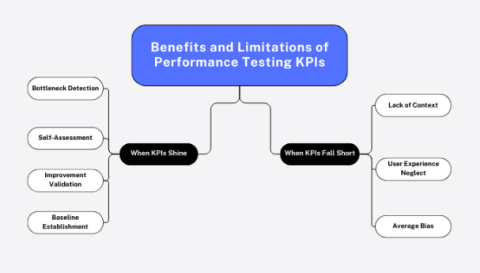
In essence, KPIs in QA testing are invaluable when used thoughtfully. Leveraging their insights, alongside user feedback and expert interpretation, paves the way for applications that not only perform flawlessly but also delight their users.
BugRaptors' performance testing services optimized a financial application for scalability and user experience. Using a Requirement Traceability Matrix and test automation ensured complete coverage and efficiency. Database testing and financial expertise addressed data concerns. Load testing identified performance bottlenecks, leading to API and query improvements and a 70% faster response time.
The client is now confident in the application's ability to handle increased user loads and meet performance benchmarks. This comprehensive approach enabled data-driven decisions for future infrastructure improvements and monitoring.
In the dynamic realm of digital experiences, QA performance testing stands as a sentinel, guarding against sluggishness and ensuring your application thrives under pressure. Through strategic implementation, careful monitoring of key indicators, and insightful interpretation of KPIs, you can unlock peak performance.
Whether aided by specialized performance testing services or empowered by test automation, QA testing is the cornerstone of delivering a seamless, satisfying user experience, fostering loyalty, and driving success in today's competitive landscape.
With more than a decade of experience in quality assurance and software testing, Kanika Vatsyayan is currently serving as Vice President, Delivery and Operations, BugRaptors. With an extensive understanding of test automation practices and advanced test approaches such as shift left and QAOps, Kanika has been actively pioneering on subjects like QA testing, AI-enabled automation, visual testing, etc. With a rich background in ensuring seamless project delivery and operational excellence, she brings a wealth of experience to BugRaptors' leadership team.


