
Updated January 2, 2025
Location data can yield valuable opportunities to engage customers – but before investing, companies must learn how the technology behind location data functions.
Location data can be very useful for app marketers. It lets companies track consumer behavior, target consumers with highly relevant messages, and much more.
From my experience at Plot Projects, a company that helps marketers include location-data technology in their apps, I’ve learned how to collect and use location data – but first, you need to understand the basic principles behind each technology.
Looking for a Mobile App Development agency?
Compare our list of top Mobile App Development companies near you
This article explains how location data technologies work, and how your business can benefit from location data.
Location data allows you to collect insights on your users’ behavior by detecting when a mobile device with your app is in a specific range.
There are two key technologies that support location data: geofencing and beacons.
A geofence is a virtual fence around a certain area. Geofencing allows you to target customers and track their behavior within a specific range.
Geofenced area can be very big (a whole city) or quite small (one store). It can have any shape you desire.
For example, a heat map of Detroit reveals a large number of geofences:
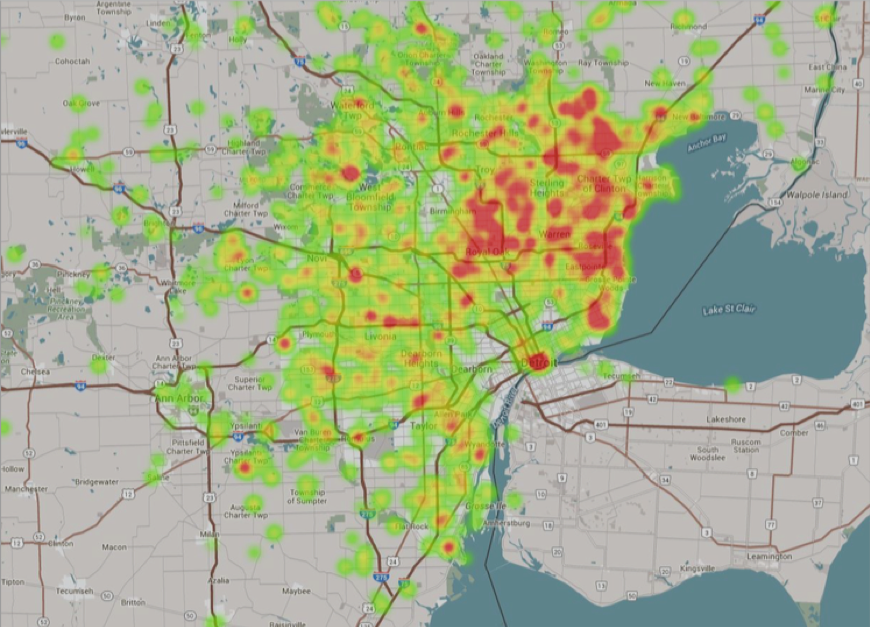
This shows how many geofences are employed in urban areas: Each green blob is a geofence. Yellow means multiple geofences cross each other and red indicates a large concentration of geofences in a certain area.
Geofencing allows you to set a virtual perimeter of any size and track and target customers within this perimeter.
A beacon is a small device that sends out a signal via Bluetooth. Beacons flag a location using a unique identifier.
Other Bluetooth devices, such as smartphones, then receive this signal if they are close to the beacon. The smartphone reacts to the signal, for example, by sending a notification.
Beacons are most commonly used within small areas, such as stores. A store can even employ different beacons for different areas within the building.
For example, imagine you run a body shop. A customer comes within range of a beacon, which encompasses the store and the immediate surroundings, and gets this message about a promotion:

A beacon is therefore quite different from a geofence: It requires a device and is used for small areas.
Geofencing and beacons have some things in common. However, they are used in different ways and rely on different technologies.
The table below outlines the major differences:
| Geofencing | Beacons | |
| Technology | Uses cellular towers and wifi to determine the user's location. | Uses Bluetooth to send its signal. Users' Bluetooth must be activated on their smartphones. |
| Location | A virtual, static area in any shape required. | The location of the device determines the perimeter; everything in range of the Bluetooth signal. |
| Static or Mobile | The geofence cannot move. | Not necessarily stationary; can be moving, such as a beacon attached to a shopping cart. |
| Target Range | Between 50 and 50,000 meters. | Between 1 and 30 meters. |
| Maintenance | No maintenance necessary because no physical device is required. | Power supply such as batteries needed; can be damaged. |
| Cost | Varies, based on the number of geofences. | Purchasing cost and maintenance of beacons. |
To select the location data technology that is right for your business, consider factors such as how you envision users interacting with location data, cost, and needed range.
Now we have seen how location data can be collected. But how can you use it?
Location data is valuable for several purposes:
Of course, these categories are quite broad. That is because location data can be used in a myriad of ways. Below, we will discuss 5 common ways businesses use location data.
Sending notifications is the most well-known way to use location data. You can reach out to customers when they enter a certain area.
Imagine for example that you are the owner of a video game store. Many of your customers are using your app to see what games are out or to check promotions. You can use geofencing to send users a notification through the app when they are in the proximity of the store.
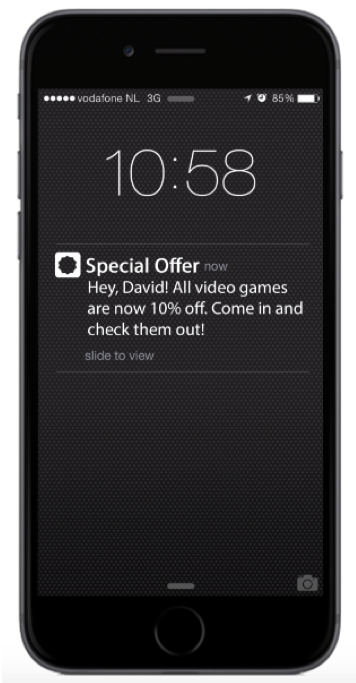
For example, you can use location data to send customers a notification informing them about a promotion or special offer.
It is possible to measure when users enter, leave, or stay within a certain area. That provides you with valuable data on users' behavior.
For example, imagine you own a store. You have an app that people use to stay up-to-date on promotions, as well as a billboard outside with a promotion for a certain product.
To use location data, you can place beacons at both the billboard and near the product. This way, you can see whether visitors who saw the billboard are more likely to check out the promoted product.
Beacons and geofencing can work together to improve smart home apps. Beacons on a small scale (room to room) and a geofence on a larger scale (to detect when someone leaves the house).
Smart home apps can use beacons to turn music or lights on when someone enters a room. The apps can also use geofences to know when users (and their smartphones) leave their home. The app can then automatically switch to “nobody's home” mode and save energy.
Online marketers are familiar with retargeting, or the process of reaching out to previous visitors to share new offers. This works well because the chance that return visitors convert is generally higher than the chances of converting new visitors.
With location data, you can apply this principle to the real world. For example, if an app user has visited a store twice, you can wait until the third visit before you give this person a coupon to try to close the sale.
This way, you are making your mobile marketing efforts more personalized while spending your budget wisely and giving out coupons to customers who are most likely to make a purchase.
We have seen how you can use location data within and around a building. However, it is applicable on a much larger scale.
By creating multiple geofences throughout an area such as a city, you can see what people’s movement patterns are over a period of time.
You can easily learn things such as what times of day or days of the week people visit a location that you are interested in.
By creating heat maps you can also see the concentration of people at a particular location. This can be useful for improving the distribution of your product or deciding where you open a new branch of your business.
You can also use this information to target customers with push notifications.
Additionally, you can use location data to inform the strategy behind where to set up a food truck, pop-up shop, sidewalk sale, or another dynamic element of your business.
Location data can benefit businesses in many ways, including targeting relevant customers, collecting valuable data, and making strategic decisions.
Whether you use geofencing, beacons, or a combination of both, location data will reveal new, useful insights about your customers.
Businesses that collect location data notice a profound impact on the success of their marketing efforts.
 Maria Golovanova is a marketing communications manager at Plot Projects. Plot Projects helps digital marketing professionals to easily integrate location-based marketing, such as geofencing, in their apps.
Maria Golovanova is a marketing communications manager at Plot Projects. Plot Projects helps digital marketing professionals to easily integrate location-based marketing, such as geofencing, in their apps.


