
Updated January 3, 2025
There is a lot of confusion and interest surrounding cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. This article explains the differences and describes the areas of impact and opportunities for business owners, including agencies and creatives.
Most people use the terms bitcoin and blockchain interchangeably, but while the sustainability of bitcoin is constantly questioned, blockchain has a strong foundation as the next long-term, stable breakthrough technology.
Although bitcoin was built on blockchain technology, it doesn't define the technology itself. It's the equivalent of calling a website the internet. While a website builds on internet technology, one application doesn't define the internet – just like while bitcoin builds on blockchain technology, one bitcoin doesn’t define blockchain.
Looking for a IT Services agency?
Compare our list of top IT Services companies near you
It's this misunderstanding that interferes with blockchain's adoption and overshadows its huge growth potential.
With over 15 years of experience in the web design and development industry, the team at Neon Rain is up-to-date with industry trends and advances in technology.
We know from our experience helping our clients with custom software development, business management systems, and process automation that blockchain technology can potentially improve your business from tracking general information to data storage and even transaction management.
Before you understand blockchain's advantages, let's understand the difference between bitcoin and blockchain.
Bitcoin is the most popular cryptocurrency on the market. It's a virtual type of currency in which encryption is used to control its storage and management.
Blockchain is bitcoin's way of verifying and storing information. Blockchain stores data in a virtual ledger, similar to an accounting ledger. Instead of one central entity controlling the ledger, each bitcoin transaction is recorded and stored by every person on the blockchain.
To better understand, imagine you get together with a group of five people to play poker, but no one remembers to bring the chips. You could each write down bets on your own piece of paper and compare notes once the game is over. Everyone reconciles his or her bets, and payouts are handed out after everyone agrees.
This is analogous to the blockchain. Everyone has his or her own wallet, performs transactions, and all nodes on the blockchain agree to add another transaction to the chain.
What makes bitcoin and other cryptocurrency users excited about blockchain is that it decentralizes control of your money.
One bank is no longer in control of how you spend, save, or pay fees. Instead, bitcoin users are in control of their own wallets, and blockchain makes it possible to keep track of transactions without the involvement of a third party controlling the funds.
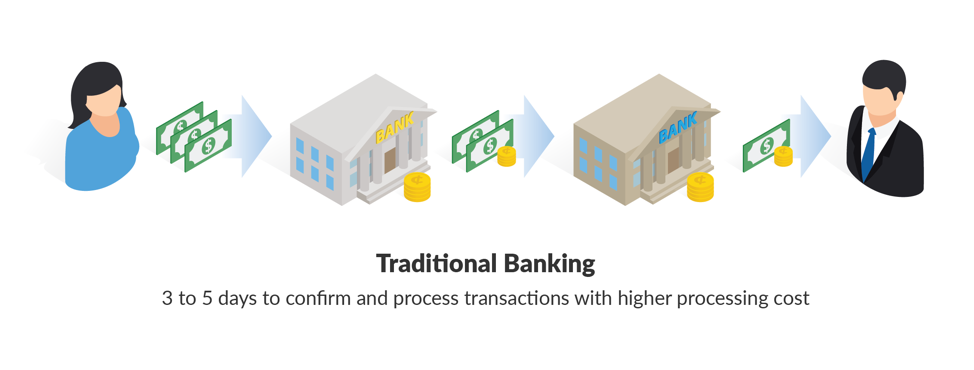
In addition, banks typically take 3 to 5 days to confirm and process transactions and have a fairly high processing cost.
Paying with bitcoin, on the other hand, takes only seconds or minutes to confirm and process a transaction.
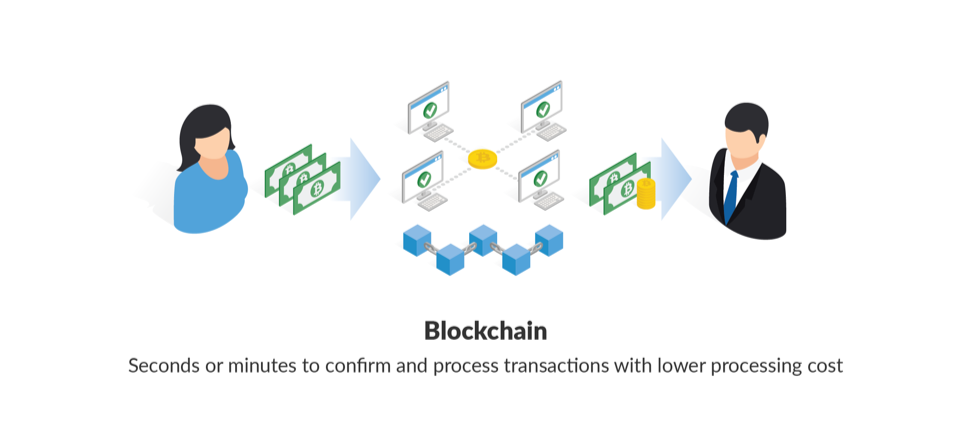
Paying with bitcoin also lowers the processing cost significantly.
Blockchain has some components of privacy, and many cryptocurrency creators have improved privacy compared to the original bitcoin.
For instance, bitcoin transactions are public and can be traced to a specific user, but some cryptocurrency creators have added ways to make transactions more anonymous and private. Some transactions are placed in a wrapper called a smart contract for privacy, but transactions are still public.
Aside from common public blockchain applications, businesses can opt for private ledgers that are inaccessible to the open public but available to select stakeholders within the organization. Although completely public blockchain technologies are usually inappropriate for private businesses, private blockchain applications offer numerous benefits, including privacy, and still offer a ledger with immutable data.
Blockchain has the potential to benefit numerous industries and improve outdated, traditional standards. Here are a few examples.
Currently, payment processors offer a way for you to take money from debit or credit cards. They only offer ways to transfer in specific currencies, and the business is limited to the types of credit cards the vendor accepts. Cryptocurrency built on blockchain technology opens a broader array of options for payment processing.
Instead of only accepting money in specific currencies, cryptocurrency is a global coin. Payments are made on the blockchain, and merchants can convert their coins to any currency they prefer at any time.
Micropayments are also available without the high fees. Credit card companies, for instance, might take 25 cents per transaction, so small transactions are costly for vendors.
With bitcoin, you can pay in micropayment up to eight decimal points, and fees are a small fraction of your transaction.
Paying with blockchain technology takes away much of the overhead of currency, credit card payments, and chargebacks. Currency is globally defined, but it can be converted into local currency after payment.
Users have money in their wallets and payments are final, so the issue of chargebacks is eliminated, and coins are accepted without dealing with credit card issues.
Traditional international payments are costly and cumbersome. Vendors get banking details from customers, and a wire transfer, direct deposit, or PayPal payment is made. Fees are about 30 cents per transaction and 3% of the total transfer.
With micropayments, this form of payment is too costly for a business, and 3% of large transactions takes a large chunk of money.
Just like micropayments for merchant processors, blockchain currency eliminates high-budget fees and reduces them to a fraction of the transaction.
Local currency is also irrelevant with cryptocurrency, but it can be converted to your currency of choice using any exchange available on the web.
Shipping and distribution data is normally stored in a central database, and we trust that the information stored isn't tampered with or corrupted.
Data integrity is integral to centralized systems where only one copy is available and only one organization controls that copy.
If you've ever ordered a product online and never received it only to have customer service tell you that "something went wrong," you understand the importance of data integrity.
With blockchain technology, anything from shipping, orders, distribution data, and sensors can be built and its data decentralized by each user containing a copy of transactions.
Because every node on the network must "agree" to changes, data integrity and trust are much higher than a centralized database. A loss of one node doesn't destroy data in its entirety.
Instead, everyone has a copy of the data, and one node can get a copy of it should theirs fail.
Smart contracts are one of the biggest benefits of blockchain technology. They are used to handle complex agreements between two or more parties.
Think of blockchain as a way to trigger specific events as each agreement is fulfilled. There are a number of ways to work with this type of application.
For example, a vendor is selling a product to a buyer who must wait for the product. The buyer creates an order, and the order triggers a request for payment. Once the buyer sends the payment, it triggers a shipping event. After the buyer receives his product, confirmation is made, and the entire transaction is complete.
With blockchain, each event is triggered, and any subsequent contract actions can't proceed until the previous event completes. It's a safeguarded way to ensure that parties agree to their end of the contract and each one receives what is promised.
Designers, content authors, logo creators, illustrators, and numerous other creatives are always fighting copyright infringement of their intellectual property.
Imagine copyright and ownership information stored on the blockchain with a public record of creative licenses and who has the authorization to use your work.
No more questionable use and confusion over who is able to use a specific asset.
Developers and programmers also fall into this category.
Software piracy is an issue for hardworking developers who must trust that users will register software instead of copying it from a third party.
By storing licenses on the blockchain, developers have a public, easily verifiable way to determine authorized purchases and detect unlicensed users.
Payments and basic smart contracts aren't the only ways blockchain is beneficial. Numerous other businesses have workflows that could be put on blockchain technology for better efficiency, tracking, integrity, and decentralization:
The possibilities are endless. Instead of thinking bitcoin when you hear "blockchain," think of the ways blockchain can improve business tracking, data storage, and transaction management.
With blockchain, businesses will find better efficiency in workflow, and data loss is far less possible.


