When you think of call centers, telephone systems, phone calls, and call center agents are probably some of the first things to come to mind. However, there is so much more to the industry than that.
This glossary intends to break down the obvious and not-so-obvious call center terms for business leaders looking to gain insight in the space. It would be difficult to engage with the BPO and call center industry without a firm understanding of key terms and phrases. We’re here to help build that knowledge.
Find and decide on the right call center company for your business on Clutch.
Looking for a BPO agency?
Compare our list of top BPO companies near you
67 Call Center Terms to Know
Call center terminology can overwhelm with acronyms and process-specific terms. However, learning foundational concepts will help you easily understand and work with call center companies.
A
- Abandoned Call: A call that is disconnected by the caller before speaking to an agent. It can be tracked as a metric to measure efficiencies at times with a high number of calls.
- After-Call Work (ACW): any administrative tasks performed by a customer service representative after they have completed a phone call with a customer. This includes recording the details of calls, updating CRM systems, and making notes on specific customer interactions.
- Automatic Call Distributor (ACD): an automated call distribution system that routes incoming calls to the appropriate call center agent. This system helps to ensure that customer calls are answered quickly and efficiently, eliminating wait times. It can also provide statistics around the number of incoming calls, wait times, and average handle times.
- Agent: An employee who handles incoming or outgoing calls on behalf of a company or organization.
- Agent Occupancy: a metric that measures the amount of time an agent spends actively speaking to customer calls in real-time. Agent occupancy is typically expressed as a percentage and calculated by dividing the total amount of time spent talking to customers by the total work time available for that day or week.
- AHT (Average Handle Time): The average amount of time an agent spends on a call, including hold time and after-call work.
- Application Programming Interface (API): a type of software that enables two applications to communicate and share data. In the context of a call center, APIs can be used to facilitate the transfer of customer data from one application to another, allowing for efficient routing of calls, automated personalized greetings, and faster resolution times.
- Automatic Number Identification (ANI): automated telephone service that identifies the number of the calling line, similar to caller id. This technology allows companies to identify, track, and route incoming calls more efficiently.
- Average Speed of Answer (ASA): The average amount of time it takes for calls to be answered by an agent.
B
- Blended Call Center: A call center where agents handle both inbound and outbound calls.
- Business Process Outsourcing (BPO): a form of outsourcing where organizations outsource part or all of their non-core processes to an external provider. Unlike call centers that provide customer service, BPO generally focuses on processes like accounting, payroll management, data entry/processing, etc.
C
- Call Blending: The process of routing both inbound and outbound calls to agents in a blended call center.
- Call Center: A facility or department that handles incoming and outgoing telephone calls for a company or organization — also referred to as contact center.
- Call Center Management: process of overseeing and managing a call center and its associated activities, including telecommunications infrastructure, customer service processes and workflows, agent training, staff scheduling, and more.
- Call Center Software: Software designed specifically for call center operations, such as call routing, CRM, and other relevant SaaS products.
- Call Logging: The process of recording information about each call in a database or system.
- Call Monitoring: The process of listening to live or recorded calls in order to evaluate agent performance, provide feedback, and ensure compliance with service level agreements.
- Call Recording: The process of recording calls for later review
- Callback: A return call made by an agent to a customer who was previously disconnected or put on hold.
- Call Queuing: The process of placing incoming calls on hold until an agent becomes available.
- Call Transfer: The process of transferring a call from one agent or department to another.
- Chatbot: a computer program that is designed to simulate intelligent conversations with users. Using natural language processing (NLP) algorithms to understand what the user says and formulate an appropriate response that matches the context of the conversation. In the context of call centers, a chatbot could be used to handle many of the simpler customer service requests, freeing up human agents for more complex tasks.
Source: Amtrak
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): A software system used to manage customer interactions, data, and automation efforts.
- Computer Telephony Integration (CTI): A technology that integrates telephone and computer systems to improve call center efficiency.
- Customer Experience (CX): the overall impression that a customer has of a company or product, based on their interactions and journeys through different channels. CX is omnichannel, considering experiences with websites, apps, physical stores, phone calls, and more.
- Customer Satisfaction (CSAT) Score: A metric used to measure how satisfied customers are with their interactions with a company or call center.
- Customer Service Representative: a service provider who works with customers to help resolve their inquiries and issues.
D
- Dialed number identification service (DNIS): a system that identifies the number dialed by a caller and provides it to the call center so that customer service representatives can tailor interactions to caller needs.
- Dialer: A software system used to dial phone numbers automatically.
E
- Escalation: The process of transferring a call to a supervisor or higher-level agent for resolution.
F
- First Contact Resolution (FCR): The percentage of calls resolved on the first attempt without requiring additional follow-up. This metric can also be referred to as first call resolution.
- Forecasting: The process of predicting call volume and staffing needs for a call center.
H
- Hold Time: The amount of time a caller spends on hold before speaking to an agent.
- Hosted Dialer: a cloud-based calling system that helps maximize agent availability by automatically routing calls to the most available agents. Hosted dialers can also offer automated call distribution (ACD) and interactive voice response (IVR), which help improve customer experience.
I
- Inbound Call: A call that a potential customer makes to a company or call center, often to inquire about promoted goods and services.
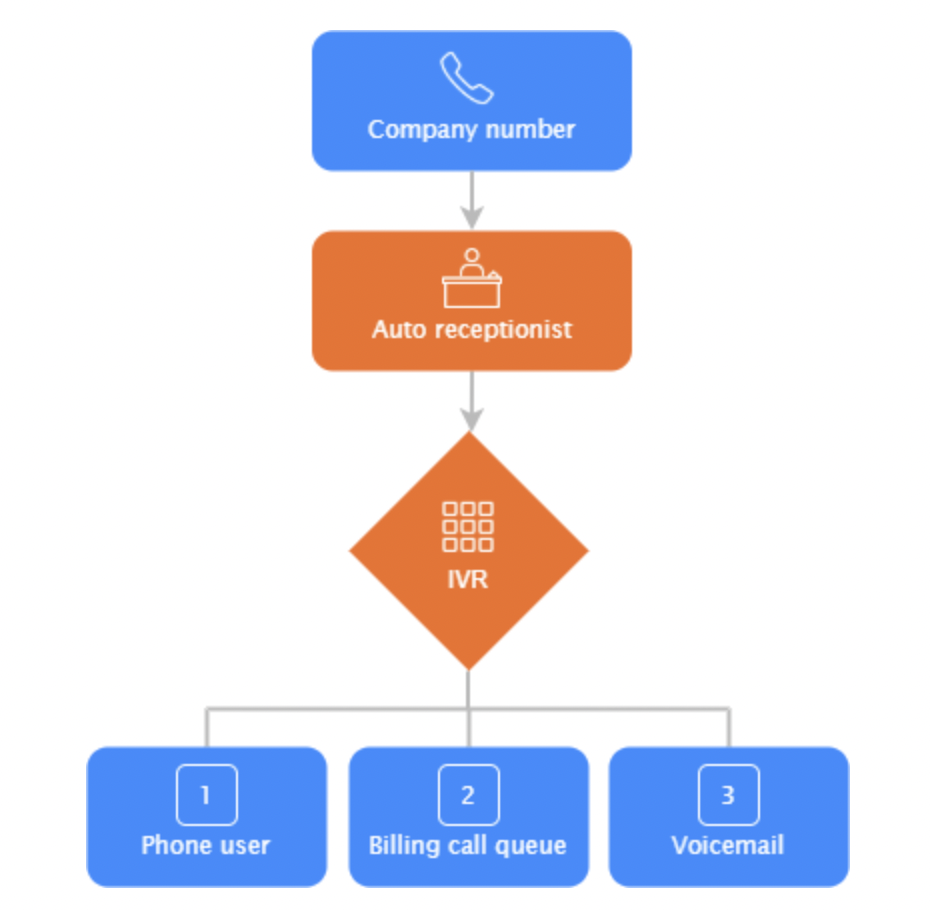
- Interactive Voice Response (IVR): A technology that allows callers to interact with a computer system through voice or touch-tone inputs.
Source: Zoom
K
- Key Performance Indicator (KPI): A metric used to evaluate the performance of a team or employee. KPIs align metrics with outputs and overall company goals.
M
- Metrics: Data used to measure the performance of a call center — examples include call volume, wait time, and abandonment rate.
- Multichannel: The ability to facilitate communication with customers over multiple channels, such as phone calls, SMS, email, chat, or social media.
N
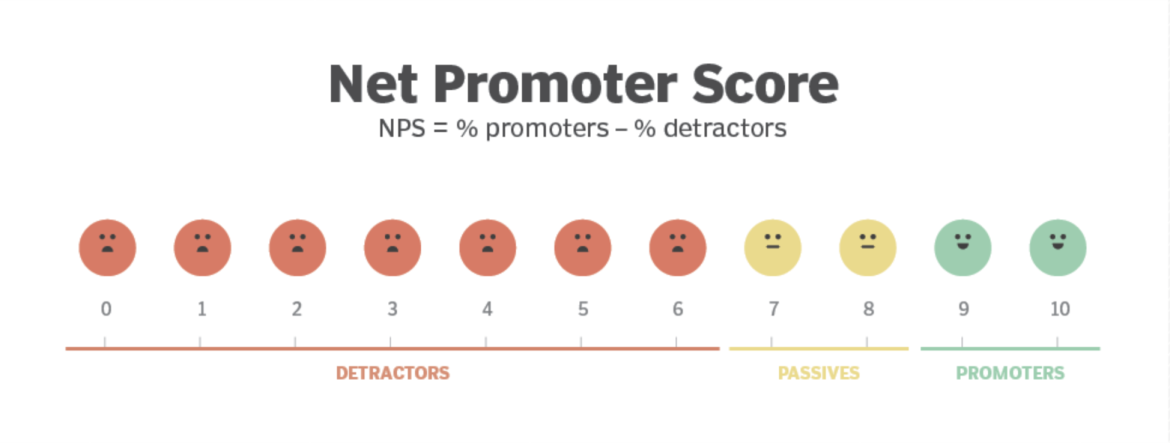
- Net Promoter Score (NPS): A metric used to measure customer loyalty and satisfaction.
Source: TechTarget
- Next Available Agent: a call routing strategy that sends incoming calls to the next available customer service representative in order to reduce wait times and abandoned calls.
O
- Offshore Call Center: A call center located in a different country than the company it serves.
- Onshore Call Center: A call center located in the same country as the company it serves.
- Outbound Call: A call made by an agent to a customer or prospect.
- Outsourcing: The practice of hiring an external company to handle call center operations.
- Overflow: The process of redirecting calls to another call center or answering service when call volume exceeds capacity.
P
- Predictive Dialer: A software system that forecasts agent availability and automatically dials phone numbers based on its predictive conclusions.
- Private Branch Exchange (PBX): an interconnected telephone system that prioritizes privacy and security, allowing businesses to communicate between offices and provide telephone access to remote employees with limited risk.
- Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN): an interconnected system of telephone networks offering secure connections with low latency.
Q
- Quality Assurance (QA): A process used to monitor and evaluate the quality of agent interactions with customers.
R
- Remote Monitoring: The process of remotely monitoring agent interactions and call center metrics for quality control and performance management.
S
- Screen Pop: a technology used in call centers that automatically displays customer data on an agent's screen when the call is connected.
- Script: A pre-written set of instructions or prompts for agents to follow during customer interactions.
- Service Level: The percentage of calls answered within a certain amount of time, typically measured in seconds or minutes.
- Service Level Agreement (SLA): An agreement between a call center and its clients that specifies service level requirements and penalties for non-compliance.
- Skill-based Routing: The process of routing calls to agents with specific skills or expertise.
- Speech Analytics: The process of analyzing recorded calls to identify patterns and trends in customer interactions using speech recognition technology.
T
- Talk Time: The amount of time an agent spends speaking with a customer during a call.
- Telemarketing: The practice of selling products or services over the telephone.
U
- Upselling: The practice of suggesting or promoting additional products or services to a customer during a call.
V
- Virtual Call Center: A call center where agents work remotely, often from their homes.
- Voice Over Internet Protocol (VoIP): communication technology that uses the internet to facilitate voice calls without a telephone line. Instead, it requires a network connection and an IP address and can be used with any device that supports the internet.
- Voice Response Unit (VRU): an automated interactive voice response system that interacts with customers over the phone. It allows for self-service transactions through voice responses and keypad selections.
W
- Wait Time: The amount of time a caller waits before speaking to an agent.
- Workforce Management (WFM): the process of optimizing operational, tactical, and strategic workforce decisions to maximize efficiency and productivity. This includes forecasting, scheduling, real-time monitoring, exception management, and reporting. Also commonly referred to as Workforce Optimization (WFO) or Workflow Optimization.
- Wrap-Up Time: The time an agent spends completing after-call work, such as entering notes or updating customer records.
Learning Call Center Terminology Makes for Smooth Collaborations
It doesn’t matter what level of service you’re looking for; you’ll have the most optimal experience with call center service providers if you take some time to understand the basics of their tools and processes.
Learning important terms will put you on the same page as your provider and help you achieve success together.
Find the call center company you’re looking for on Clutch.
About the Author
Sydney Wess
SEO Manager at Clutch
Sydney Wess is a SEO manager who focuses on strengthening organic performance and building topical authority for Clutch.
See full profile
![How to Create a Corporate Training Budget [With Template]](https://img.shgstatic.com/clutch-static-prod/image/resize/715x400/s3fs-public/article/f8cb0a8fb8e36a14ff257e02ce8b9475.jpg)
![How to Create a Corporate Training Budget [With Template]](https://img.shgstatic.com/clutch-static-prod/image/resize/715x400/s3fs-public/article/f8cb0a8fb8e36a14ff257e02ce8b9475.jpg)



![How to Create a Corporate Training Budget [With Template]](https://img.shgstatic.com/clutch-static-prod/image/resize/715x400/s3fs-public/article/f8cb0a8fb8e36a14ff257e02ce8b9475.jpg)

