
Updated August 6, 2025
Regulated industries, including fintech and healthcare, consistently prioritize security. This article examines the reasons why Flutter is a sensible option for building safe applications in these high-pressure settings.
The handling of user data and system integrity is a constant source of scrutiny for fintech and healthcare organizations. Development teams in these domains require tools that facilitate stringent compliance without sacrificing usability or speed when creating mobile applications.
It’s not fancy features that build trust; it’s security. In such sectors as finance and healthcare, mobile apps manage everything from banking information to personal health records, and users demand unwavering speed and data safety.
This is why you need to plan thoroughly when choosing the framework for your application. Flutter is an excellent choice that can help with mobile app security for healthcare and fintech.
Looking for a Mobile App Development agency?
Compare our list of top Mobile App Development companies near you
Flutter's polished user interface and rapid development have helped it gain popularity in the mobile space. Based on the Developer Survey 2024 by Stack Overflow, 9.4% of developers work with the framework. Meanwhile, Statista’s 2023 data shows that Flutter is the tool of choice for cross-platform development, as voted by 46% of software engineers.
In this article, we will shed light on the benefits of employing Flutter for building mobile apps in industries where security always comes first.
Even a minor hack can result in legal action or penalties and long-term harm for apps that store financial or health information. This means that there is no place for shortcuts under strict regulations like HIPAA, GDPR, and PCI DSS. At the same time, attacks are becoming more sophisticated and aiming at both user devices and app logic.
It’s sufficient just to look at recent examples. In May 2025, Coinbase, one of the largest cryptocurrency exchanges, reported a major data breach that involved bribed contractors, compromised personal data, and a demand for a huge ransom. Earlier this year, Hillcrest Convalescent Center in North Carolina announced an incident that resulted in stolen data of over 100,000 individuals.
Before building a fintech or a healthcare application, the essential thing to do is to get acquainted with the strict industry regulations – these vary from country to country. We break down the basics.
Fintech businesses manage funds, identities, and all digital traces connected to financial transactions. That presents a significant challenge for developers as well as an alluring playground for cybercriminals.
As a result, fintech apps must adhere to multiple regional and international standards. The most well-known are:
Authentication processes need to be flawless, while both at-rest and in-transit data should be protected. Additionally, the application must be able to identify odd activity while keeping the app running normally.
In the United States, apps that handle protected health information (PHI) must adhere to HIPAA regulations.
Europe demands adherence to the GDPR. It introduces additional layers of consent, data minimization, and the "right to be forgotten". The latter allows individuals to request the deletion of their personal data under certain conditions.
Depending on the region, developers may also face local laws like Canada’s PIPEDA or Brazil’s LGPD.
As mentioned above, regulations vary by country, so it’s essential to familiarize yourself with them before developing an application.
Here's a visual comparison of the core regulatory and security challenges across fintech and healthcare sectors:
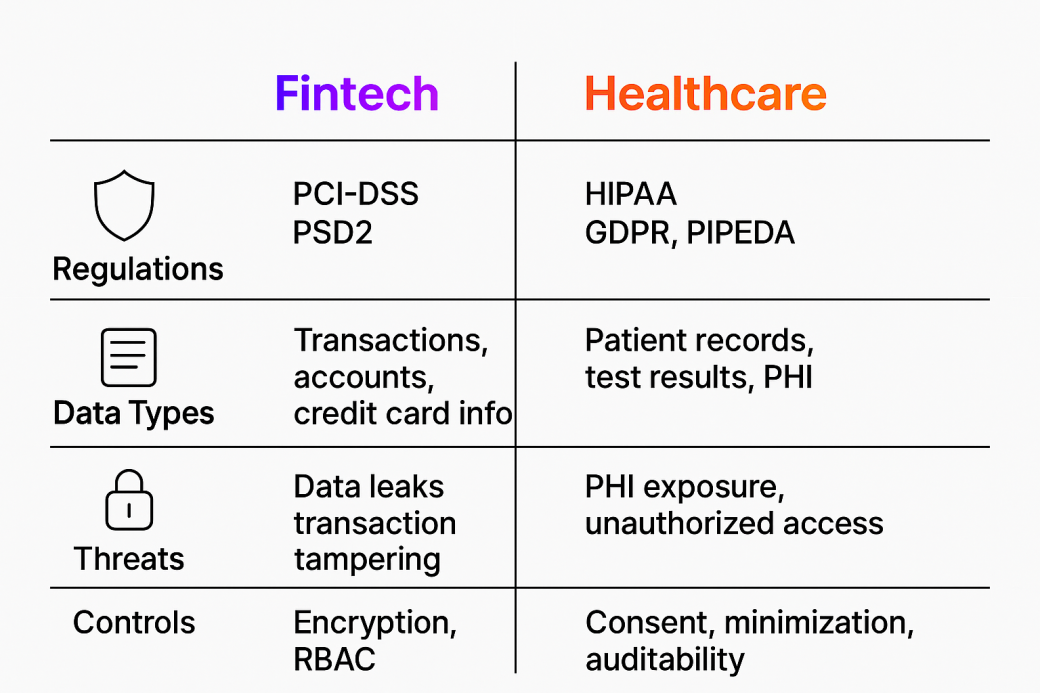
However, people are not protected by rules alone. An application's security posture is shaped by every detail, such as how it manages sign-ins, stores data, and interacts with servers. Healthcare is the industry that leaves no room for guesswork, as any weakness can become a liability.
Complying with legal requirements is only one aspect of security in regulated industries. The proper fusion of internal procedures and technical solutions is also necessary for strong protection.
Developers and other stakeholders in regulated industries can’t afford to ignore the four serious mobile security threats listed below.
Exposure of financial or personal data can lead to consequences that extend beyond mere adherence to the law.
In the medical field, this might mean granting access to patient records or allowing third parties to view private test results. In fintech, attackers may find transaction logs, credit card information, or other private data in fintech, which frequently results in a decline in customer confidence, monetary losses, or interruptions in service.
Common ways for data to leak include:
Notable examples of data breaches include Finastra, one of the world’s largest fintech providers. In November 2024, the company suffered a major data breach that affected over 800,000 individuals in the United States alone. As reported, the attackers allegedly used compromised credentials to access Finastra's Secure File Transfer Platform (SFTP).
Mobile applications use inter-process communication to interact with the system and other apps. If that communication isn't properly validated, attackers may step in. A malicious app could fool a legitimate one into revealing private data or carrying out illegal instructions.
Unfortunately, these attacks are frequently undetected until something goes wrong, like a payment being redirected or private messages appearing on the incorrect screen.
For instance, 1Password 8's macOS XPC IPC interface lacked adequate validation. Local attackers may have taken advantage of this vulnerability to steal the contents of the vault. Although no cases were reported, the vulnerability was regarded as very serious.
In modern apps, passwords are still used to secure access, but they are frequently not enough. Hackers often obtain admin-level rights through weak or outdated login procedures. They can also impersonate users or take advantage of session tokens. Applications frequently neglect access control, and that leaves room for privilege escalation and data misuse.
As an example, we may look at the hack on the Australian insurance company Medibank. The company didn't mandate multi-factor authentication for its employees, and hackers were able to access its customers' personal data. Consequently, the data of 5.1 million current and former Medibank customers made its way to the dark web.
Attacks never originate only from the outside. Sometimes, malicious actors embed malware inside apps that look trustworthy but are, in fact, compromised. This malware can silently transmit data in the background, listen to unencrypted traffic, and record keystrokes.
There is also reverse engineering. When used for a good cause – like in the case of WannaCry – it’s a great method of finding security flaws in an application. But often attackers dissect an application's code to find hardcoded keys, business logic, or vulnerabilities that are buried deep within the stack. Consequently, they can break your app once they understand how it operates.
Why Flutter Is the Best Choice for a Safe App
To begin with, Flutter applications are compiled into native machine code ahead of time (AOT). This implies that hackers won't find any intermediate bytecode lying around. The standard features of obfuscation and code minification make it more difficult for someone to try to reverse-engineer the application.
Flutter’s architecture is layered, which means engineers have direct access to widgets, rendering, and platform integration. The framework follows platform-specific practices and is tightly coupled with native elements. Standard security features of iOS and Android – like Keychain and Keystore – are directly integrated into the Flutter-powered app’s logic.
For storage of sensitive information, Flutter employs AES-based encryption. This approach enables developers to work with encrypted data at rest. Even if the app is compromised, it's not easy to retrieve data that can be used. The user maintains control by limiting access to storage through device-level authentication or biometric checks.
Overall, Flutter gives control to the developers. It offers them both the structure and the freedom to make security decisions that match the regulations they are facing.
One more advantage? Consistency. It is maintained by a unified codebase for iOS and Android. Flutter simplifies audits and compliance reviews as it eliminates the need to track changes in two different ecosystems.
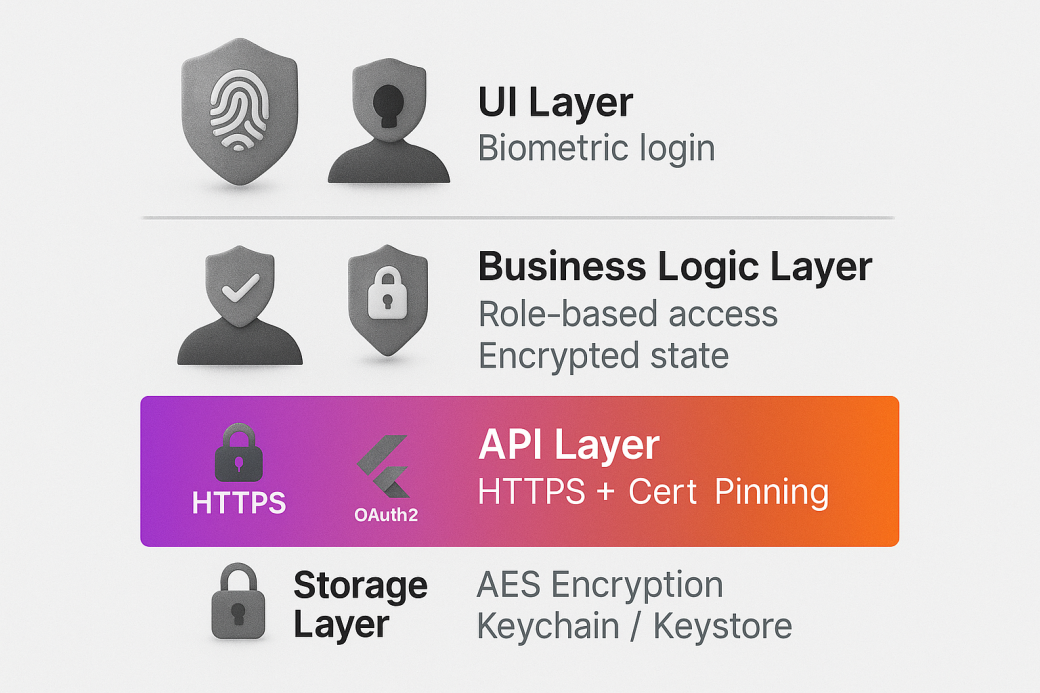
Even though no framework is perfect right out of the box, Flutter establishes a solid foundation for secure applications. When combined with a secure mobile app architecture, it provides exactly the experience that users of fintech and healthcare have become accustomed to.
In addition to keeping up with industry standards, Flutter offers development teams the resources they need to directly address compliance requirements. Here's how it incorporates intelligent integrations and supports essential components.
Flutter facilitates strong authorization flows with OAuth2 and OpenID Connect through trusted libraries like AppAuth and openid_client. These protocols securely manage token-based access and integrate well with frameworks that require a high level of compliance. These standards provide your users with transparent, controlled access to essential information.
With local_auth, Flutter not only makes biometric login possible across platforms but also guarantees its reliability. In Flutter-fueled healthcare apps, private patient information is secured with the user's fingerprint. In fintech, biometric authentication serves as a safeguard against unauthorized logins on the ledger.
Due to Flutter's flexibility, applications can use audit logging frameworks that track user actions, permission changes, and access history in real time. When you combine that with role-based access control systems, you can clearly define who can view or edit important data. Every access point can be tracked and reported on as needed, whether it's a finance manager looking at transaction histories or a doctor updating patient notes.
So, what does it take to build a secure Flutter-powered application? Let’s take a look at three approaches that are considered the pillars of Flutter security.
Flutter compiles to native machine code. Unfortunately, that doesn’t make it one hundred percent safe from attacks. One should take extra precautions to keep the application safe from attackers who could reverse-engineer it.
One of such methods is code obfuscation. It alters the output and makes it difficult for people to comprehend. Because of this, if someone can access the application, they will not see logical reasoning but rather unintelligible nonsense.
Here’s a tip: Prevent prying eyes from easily reading your application logic by scrambling and hiding your Dart code with tools like flutter build apk—obfuscate— split-debug-info.
Apart from obfuscation, use anti-tamper libraries that look for indications of app modification, like different checksums or mismatched signatures. These safeguards detect attempts to repackage or insert malicious content into your app.
The Dart ecosystem includes tools like Flutter Secure Storage and ProGuard (for native Android builds) to further tighten the security.
Data rests, changes, and occasionally lingers longer than it should in an application. There are steps to implement that can change that.
A thing to remember – secrets should never be stored in persistent memory or static variables.
In regulated industries, demonstrating security both in writing and in code is just as important as simply knowing what is secure. That’s why audits are a vital component of a healthy development cycle.
Here’s the plan for managing your app’s security through audits and testing:
Resources such as the OWASP MASVS guidelines or the MobSF (Mobile Security Framework) offer a solid basis for organized assessments.
Flutter's ability to handle the difficult tasks – end-to-end encryption, biometric integrations, secure API communication, and consistent user journeys across Android and iOS – quietly is what sets it apart. The framework won’t create a secure app for you, but it will give your development team a solid basis for building one.


