If you’re new to SEO, it’s easy to get confused by the lingo and terminology. This glossary defines some of the most common terms used by SEO professionals to help you optimize your website.
Search engine optimization, better known as SEO, is key to growing your business’s online visibility and increasing traffic to your website. Yet, many people don’t know where to start when optimizing their websites.
This glossary defines common SEO terms that you need to know whether you’re optimizing your website yourself or are working with a digital marketing firm.
Looking for a SEO agency?
Compare our list of top SEO companies near you
Looking to hire an SEO firm? Connect with top service providers on Clutch. Then filter by location, price, and review ratings to find the perfect partner for your project.
92 SEO Terms to Know
These 92 terms are essential to understanding SEO.
A
- Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP): AMP is an open-source framework that Google launched in order to create mobile-friendly websites that load quickly.
- Algorithm: How search engines find and rank content for search queries. The algorithm factors in information such as content quality, relevance, user experience, images, and domain authority.
- Algorithm Update: Search engines, such as Google, update their algorithm to improve performance and provide better search results.
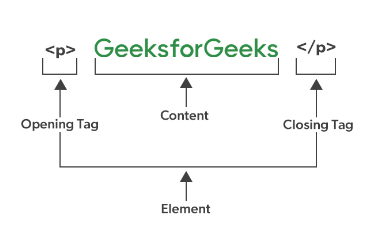
- Alt Text: Alt text is an alt attribute in HTML and XHTML documents used to describe webpage elements such as images. This helps crawlers understand the page’s content and is displayed if the elements can’t be rendered. It also improves webpage accessibility.
- Anchor text: Anchor text is visible and clickable text for a link. When clicked, it will redirect users to a desired webpage.
B
- Backlink: A backlink is a link from an external site. Also known as an inbound link.
- Bing: Bing is a seach engine owned by Microsoft.
- Black hat SEO: SEO tactics that violate webmaster guidelines. For example, spammy links, invisible text, keyword stuffing, and link swapping.
- Bots: Bots — short for robots — are computer programs that imitate human activity on the internet.
- Bounce Rate: The percentage of website visitors who leave a webpage without
- Breadcrumb: Breadcrumbs are a navigational feature on many websites that allow users to keep track of their location on a website.
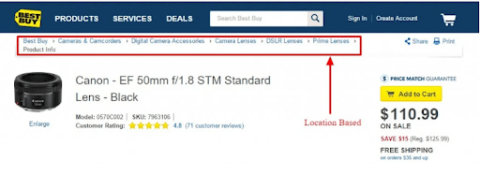
Source
- Broken Link: When a URL is not accessible to users or can’t be found by search engines, it’s known as a broken link. Often, users will receive an error message when they click on a broken link.
C
- Caching: A cache stores a subset of data on a website. This helps website speed so users are able to access data faster on the primary storage location.
- Caffeine: Caffeine is the name of Google’s indexing system.
- Canonical: A Canonical URL is an HTML link element that is used to tell search engines and web crawlers which version of a webpage should be indexed.
- Citations: Citations are mentions of a business’s information — such as their name, address, and phone number (NAP)— on site other than their own. They’re often found on directory pages.
- Click-through Rate: CTR is the percentage of people who click on an ad or call-to-action (CTA). It’s calculated by dividing the number of people who click on an ad by the number of impressions on the ad. Then multiple by 100.
CTR= (Clicks/impressions)x100
- Cloaking: Cloaking is when a webpage’s content is different from how it is presented to search engine crawlers. The goal for this is to improve the page’s search engine rankings, but is considered a black hat SEO tactic.
- Crawl Budget: Because search engines have a limit on how many pages they can crawl on a website, each platform has a limit for the number of pages that will be crawled within a certain time period. To improve rankings, SEOs have to
- Crawler: A web crawler is a bot that searches and automatically indexes web content so it can be found on search engine results pages.
- Crawler Directives: Crawl directives are the various ways you can tell crawlers how to scan your site. For example, you can tell a crawler not to scan a page, not to index it, or to follow links on a certain page. This can be used to help manage crawl budget and make sure only useful pages appear on SERPs.
- Crawling: A verb referring to the process in which bots (or crawlers) discover and index webpages.
D
- De-Indexed: De-indexing is the process of removing a page that has already been indexed from search engine results.
- Domain Authority: Domain authority (DA) is a scoring system that was developed by Moz in order to measure the credibility of a site and the likelihood of it ranking on SERPs.
- Duplicate Content: When the exact same content is available on multiple webpages and websites, it is known as duplicate content. Usually, this impacts rankings and will make it less likely for both pages to rank on SERPs.
E
- Engagement: User engagement is a metric that calculate the average amount of time a user spends on a webpage or website. It can also refer to other types of user engagement such as commenting or liking on social media.
- External Link: any link that exists on another domain and redirects users back to your website.
F
- Featured Snippet: A feature on Google SERPs that shows the description of a search result before the link and at the top of the results page.
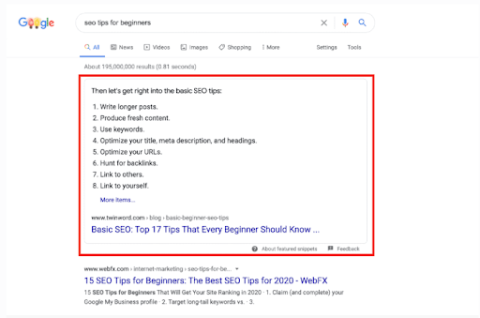
Source
G
- Google Analytics: An analytics platform that tracks and reports website traffic.
- Google Bot: The name of Google’s crawler.
- Google My Business: GMB is a tool that Google offers to allow local businesses to manage their business’s information line. Business listing include a business’s name, address, phone numbers, and hours of operation. It can help these businesses appear in search results and on Google Maps.
- Google Search Console: GSC is another Google tool that can help track search performance and traffic. However, it is also particularly useful for fixing technical SEO issues on your website.
H
Source
I
- Image Carousels: An image carousel is a website feature that is used to present images in an engaging way. It is similar to a slideshow in that it cycles through several images, but users can also click on buttons to see new images in the carousel. It can also refer to a Google SERP feature that acts the same way.
- Indexing: Indexing refers to how crawlers organize webpages on the internet.
- Internal Links: Internal links are when a link directs users to another webpage on the same website. They’re important because they help both users and crawlers discover content on your website.
- Inbound Links: Inbound links are links from another website to your website. Also known as a backlink.
J
- Javascript: Javascript is a scripting language that is used to create dynamic webpage content.
K
- Keyword: A keyword refers to an idea or topic. Keywords are used to describe the content on a web page, but also refers to what terms users search. Many digital marketers optimize content on their website to target keywords that users search.
- Keyword Density: Keyword density is the ratio between the number of times that a keyword appears on a webpage and the total number of words on that page. While a page has to contain the targeted keyword to rank, it cannot be overused less it be considered keyword stuffing.
- Keyword Research: The process of finding potential search queries, also known as keywords, to target. To assess the validity of a keyword, digital marketers need to know roughly the search volume of the keyword as well as how difficulty it is to rank.
- Keyword Stuffing: The overuse of a keyword or phrase within content. It is considered spam and is a negative ranking factor.
L
- Landing Page: A standalone webpage that users lands on after they click on a link. It can be used for an email, social media, or PPC ad campaign.
- Link Building: The process of earning external links, or backlinks, to your website. This can help crawlers discover content on your website and build credibility for your brand. Some popular link building strategies include content marketing, public relations, and email outreach.
- Long-Tail Keywords: Long tail keywords are longer search queries that usually contain 3–5 words or a full phrase. They target niche audiences and often have a lower search volume, but lower keyword difficulty.
M
- Manual Penalty: Manual penalties are issued when a website is not in compliance with Google’s webmaster guidelines. Unlike an automated penalty, these penalties are issued by a human reviewer.
- Meta Description: A meta description is an HTML element that utilizes a meta tag. It’s valuable because it summarizes a webpage’s content and is often displayed on SERPs to give users an idea of what the page is about.
- Meta Robots Tag: A meta robots tag is an HTML tag that provides crawler directives to adjust how SERPs present content in search results. For instance, a robots.txt file tells crawlers which URLs can be accessed on your website.
- Meta Tags: Meta tags are HTML tags that appear in a webpage’s source code.
N
- Navigation: Website navigation describes how users find new pages on a website. It is closely tied to a website’s information architecture but is created by a combination of links, menu items, search bars, and filters.
- NoFollow: NoFollow links are links that use a rel=”nofollow” tag to tell crawlers to ignore that link. Unlike normal links, NoFollow links do not pass ranking power (aka “link juice”) to the page they link to.
- Noindex: A Noindex tag tells crawlers not to index that web page so they dont appear on search engine results pages (SERPs).
O
- On-Page SEO: On-page SEO refers to optimizing and making changes to your own website to improve search engine rankings.
- Organic Search Results: Unpaid listings (not ads) that appear on search engine results pages.
- Organic Traffic: Clicks to your website that come from organic search results.
- Outbound Links: Links that direct users from your website to another.
P
- PageRank: PageRank is the name of a Google algorithm that is used to rank webpages. As one point, PageRank was also a toolbar that assigned a score to represent the importance of a URL. The higher the PargeRank score, the more authoritative the site was considered.
- Page Speed: The amount of time it takes for a URL to load. It does impact user experience, and therefore, SEO.
- Panda: Panda is a Google algorithm update that was originally launched in 2011. It helped put higher-quality content at the top of results pages by lowering the rank of webpages with thin or low-quality content. It is still included in Google’s current algorithm.
- Penguin: a 2012 Google algorithm update that was intended to eliminate spammy content. It is still included in Google’s current algorithm
- People Also Ask: A rich snippet feature on Google that populates additional questions related to a search query.
Q
R
- Rankings: See “Search Engine Rankings”
- Redirects: Redirects are used to redirect users to a different URL.
- Referral Traffic: website traffic that comes through another source such as an external link.
- Rich Snippet: A Google results feature that provides additional data from the page’s structured data.
- Robots.txt: Robots.txt is a file that indicates which URLs crawlers can access on a website.
S
- Schema: Schema Markups are microdata, or tags, that people can add to the HTML of a webpage to improve how crawlers analyze a page.
- Search Engine Rankings: The order of how webpages are listed on search engine results pages (SERPs).
- Search Engine Results Page (SERPs): The page that search engines serve based on the search query.
- Search Intent: describes the user or audience intent when they submit a search query.
- Search Query: the keyword, term, or phrase that a user enters into a search engine.
- Search Volume: how many people search a term every month.
- Sitemap: a file that includes all of the pages, videos, and other files in a website, as well as how they’re connected. It acts as a blueprint for yor website and helps search engines crawl and index content.
- Snippet: Refers to featured snippets on search engine results pages. They are highlighted excerpts of text from online content that appear before organic search results.
- Status Code: HTTP status codes are response codes that are issued by a server. They indicate whether a request can be filled, and if not, what the primary issue is.
Common Status Codes
- 2XX Status Codes: The request was successful.
- 3XX Status Codes: a status code that indicated that additional action needs to be taken for the request to be completed.
- 4XX Status Codes: A status code that occurs than a webpage doesn’t exist or is restricted.
- 5XX Status Codes: There was a problem with the server that prevented the request from being executed.
T
- Title Tag: an HTMl element that identifies the title of a web page.
- Traffic: Website traffic is a metric that represents the number of visitor to a website or webpage.
U
- User Experience: User experience, or UX, is the overall usability of a website. It encompasses everything from interface design to navigation, ease of use, and more.
W
- Webmaster Guidelines: Guidelines for providing helpful, reliable, and useful content online. To rank well, a website needs to follow webmaster guidelines.
X
- XML: XML stands for extensible markup language, a markup language used to define and store data.
- X Robots Tag: An alternative to a meta robots tag, an X-Robots-Tag is included in HTTP headers to control the indexation of a webpage.
Y
- Yahoo: A popular search engine.
Understanding the Terminology in SEO is Essential For A Seamless Partnership
For those who aren’t SEO experts, it can be challenging to follow the issues and strategies their digital marketing counterparts are utilizing to optimize their website for search. Knowing the definitions and having a basic understanding of the terminology associated with this process is essential to communicating between teams. Hopefully, this glossary has clarified some of the terms your SEO team uses regularly.
Looking to hire an SEO firm? Connect with top service providers on Clutch. Then filter by location, price, and review ratings to find the perfect partner for your project.
About the Author
Hannah Hicklen
Content Marketing Manager at Clutch
Hannah Hicklen is a content marketing manager who focuses on creating newsworthy content around tech services, such as software and web development, AI, and cybersecurity. With a background in SEO and editorial content, she now specializes in creating multi-channel marketing strategies that drive engagement, build brand authority, and generate high-quality leads. Hannah leverages data-driven insights and industry trends to craft compelling narratives that resonate with technical and non-technical audiences alike.
See full profile