
Updated June 26, 2025
Google knows that context matters for query results. The search engine uses updated algorithms and practices to determine the contextual meaning behind keyword-based searches.
Updated September 18, 2023
In a blog post, Bill Slawski, director of SEO research for Go Fish Digital, said “context” was the SEO buzzword of 2018. Years later, context with content marketing is still considered king when it comes to what is ranking on SERPS (search engine results pages).
Looking for a SEO agency?
Compare our list of top SEO companies near you
While most online searches are based on keywords, search engines are moving onto better practices—algorithms—to present their users with more relevant content.
Consequently, search queries increasingly rely on context, not just keywords, to produce results for web pages.
For example, the word “python” describes a venomous snake as well as a famous programming language. As a remedy, Google has implemented a series of patents and algorithms in the last 20 years to capture the intent behind users’ queries.
Hire an SEO firm to assist with your company with Google search.
Context vectors are vector representations used to retract similar words. Google recently patented "context vectors" to index a database of content via knowledge bodies such as Wikipedia.
Google will be able to embed a wide variety of written language into vectors by getting a patented AI under its RankBrain algorithm, which will help make user searches more contextually relevant.
Google will also factor users’ other inputs to identify intent—whether the user is searching for “Python” or “python.”
Under this patent, a search result might show additional relevant content from comparable searches. To better understand this feature, input “tallest building in America” into the search engine.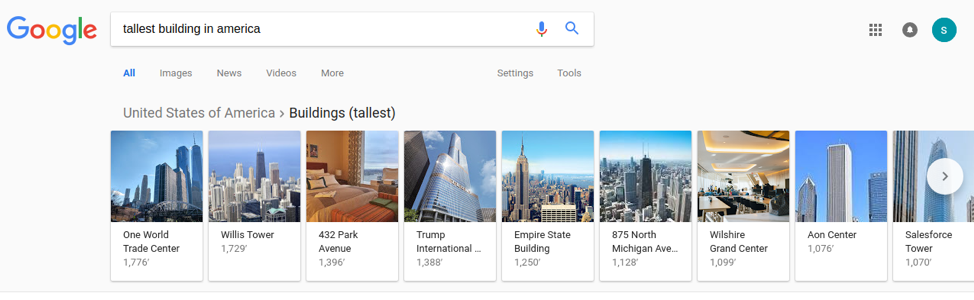
Google provides an answer but also shows how that structure compares to similar ones. This visual comparison makes the achievement relative to its competition and more accurately reflects the nature of the user's curiosity.
Google refreshed its “people also searched for” feature to focus on context for searchers. Google built this function on a content vector to provide a better experience in the same mode as the comparative building images.
Take a search for Lord Buddha’s birthplace as an example.
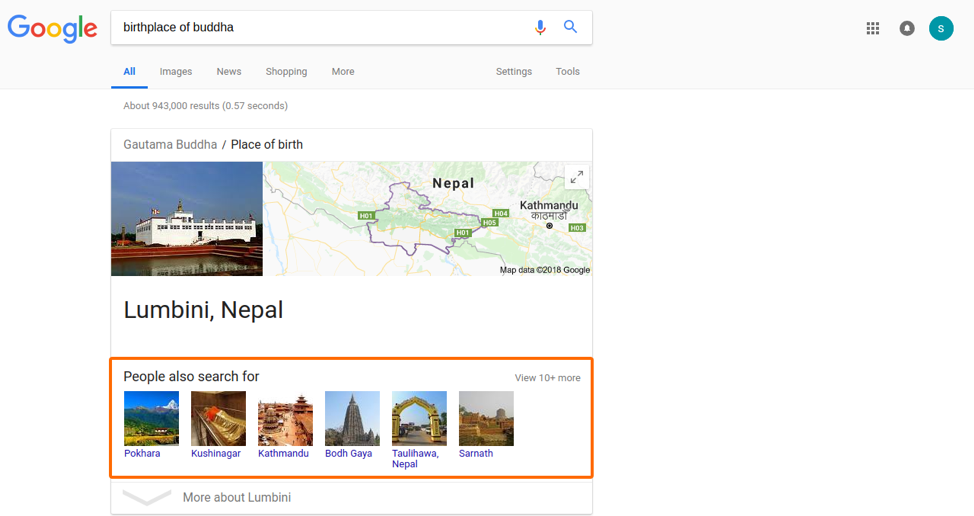
The answer appears in Google’s knowledge panel, a box that is located on the first search result page, powered by the Google knowledge graphs. But in addition to the answer, Google also displays what other people searched for in Nepal.
The results anticipate the user's desire to travel to Lord Buddha’s birthplace and displays useful links for planning such a trip. All of these results could vary in search volume and related keywords, but are able to capture the search intent of specific target audiences.
Black hat practices refer to aggressive SEO tactics that attempt to improve rankings by disregarding the audience and search engine guidelines. Google had been aware of these practices and webmasters’ tendencies to indulge in them. Google has fought against these practices like other search engines by updating its algorithm with new releases.
The Panda update was Google’s initial attempt to provide better search results by making quality content a necessity for high rankings.
Panda enabled websites that posted legitimate and helpful content to gain authority. The algorithm also punished sites that either copied other sites' content or published low-quality content stuffed with keywords.
Penguin was the next iteration after Panda.
In addition to combatting low-quality content, the algorithm focused on punishing sites involved in black hat SEO practices. Google monitored keyword stuffing, link spams with backlinks, and doorways pages, decreasing a company's rank if it followed fraudulent practices.
Hummingbird completely overhauled the previous set of algorithms. This release marked Google’s shift from target keywords to user intent as the main ranking factor. As a result, Hummingbird ranked search results by relevance more than content.
But this change also affected how users found information online and their overall user experience navigating relevant results.
Google doubled-down on machine learning and natural language processing with its Rankbrain release. Rankbrain interpreted queries, no matter how obscure, and aimed to match them quickly to the best possible results.
The algorithm also monitored user behavior and downranked less relevant pages. The tool used activity from similar searches to achieve this function.
As search evolves, Rankbrain has paved the way for Google to understand the context of a search query and show results accordingly.
Many marketing strategies do focus on keyword research when it comes to content creation, but when it comes to search engine optimization, teams avoid certain tactics that can be seen as black hat that Google discovers.
To not be penalized by Google, avoid the following:
An ever-increasing number of people use voice searches. Google Assistant, the company’s voice-enabled AI tool, capitalizes on this popularity. Users say “OK Google” to initiate a voice-based search.
Additional Reading: ‘Voice Search Statistics: How Do People Use Voice Search?’
Google Assistant, available on mobile phones and smart home devices, is set to disrupt the search engine experience. However, these advances wouldn’t be possible without previous algorithm tweaks that located the implicit context in user queries.
In 2023, Google launched their own AI-based chatbot, Bard.
In this decade, search results have moved away from keywords and focused more on the context behind users’ inquiries. This transition has compelled Google to create algorithms that respond to user behavior and activity.
Websites have a role in this shift as well. To capture current SEO practices, sites must understand the context surrounding users’ intent, especially for targeted audiences. When crafting their content strategy, marketing teams have to start realizing optimization needs more than keywords to earn top results.
New analyses and strategies may be necessary to achieve even better SEO.


